基础
图就是多叉树的延伸,
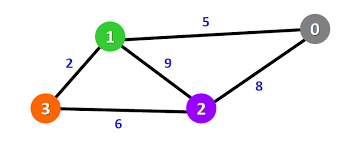
多叉树 & 图:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
class Vertex {
int id;
Vertex[] neighbors;
}
class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode[] children;
}
|
建图 和 建表
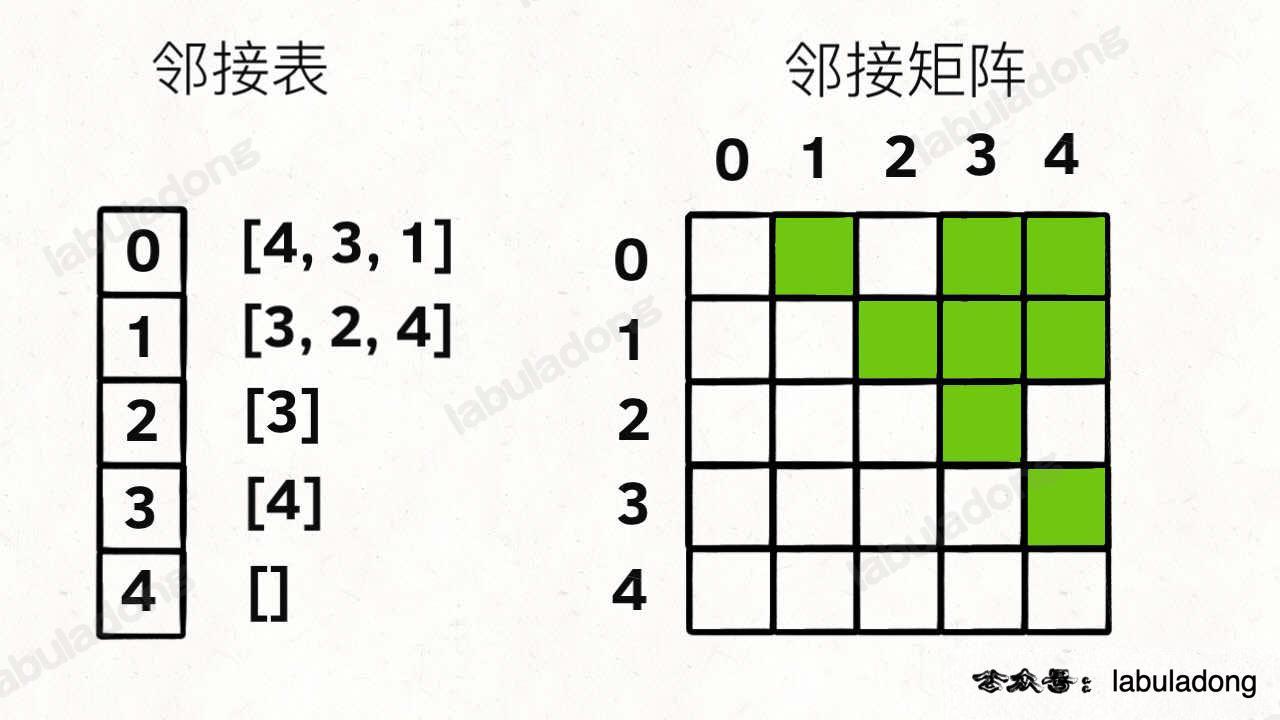
邻接表:我把每个节点 x 的邻居都存到一个列表里,然后把 x 和这个列表关联起来,这样就可以通过一个节点 x 找到它的所有相邻节点。
邻接矩阵:一个二维布尔数组,我们权且称为 matrix,如果节点 x 和 y 是相连的,那么就把 matrix[x][y] 设为 true(上图中绿色的方格代表 true)。如果想找节点 x 的邻居,去扫一圈 matrix[x][..] 就行了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
List<Integer>[] graph;
boolean[][] matrix;
|
建图建表的优劣:
邻接表:占用空间少,但是无法快速判断两个节点是否相邻
邻接矩阵:空间占用高,但是可以快速查找相邻节点
比如判断节点 1 是否和节点 3 相邻,我要去邻接表里 1 对应的邻居列表里查找 3 是否存在。但对于邻接矩阵就简单了,只要看看 matrix[1][3] 就知道了,效率高。
除链式前向星外:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| private void buildGraph(int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
}
private void add(int from, int to) {
graph.get(from).add(to);
}
|
度
入度 和 出度
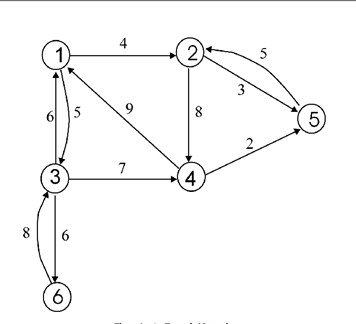
由于有向图的边有方向,所以有向图中每个节点「度」被细分为入度(indegree)和出度(outdegree)
上图中的3的入度为3出度为1
加权
邻接表:
存储不单单邻居节点还存储权重
邻接矩阵:
matrix[x][y] 不再是布尔值,而是一个 int 值,0 表示没有连接,其他值表示权重
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
List<int[]>[] graph;
int[][] matrix;
|
无向
无向图 == 双向
邻接表:
在 x 的邻居列表里添加 y,同时在 y 的邻居列表里添加 x
邻接矩阵:
把 matrix[x][y] 和 matrix[y][x] 都变成 true ;
遍历
遍历(多叉)树结构时,我们有:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
void traverse(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
for (TreeNode child : root.children) {
traverse(child);
}
}
|
由于图可能包含环,所以为了避免无限遍历我们需要一个visited数组来表示已经遍历过:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
boolean[] visited;
boolean[] onPath;
void traverse(Graph graph, int s) {
if (visited[s]) return;
visited[s] = true;
onPath[s] = true;
for (int neighbor : graph.neighbors(s)) {
traverse(graph, neighbor);
}
onPath[s] = false;
}
|
注意,visited数组不需要撤销操作,这是因为我们需要始终记录已经遍历过的节点;而 onPath 数组需要撤销操作从而保证遍历了每一个节点,但是注意的是回溯中撤销的是枝干,因此在for循环里面,但是这里的dfs关注的是节点,因此在for循环外面
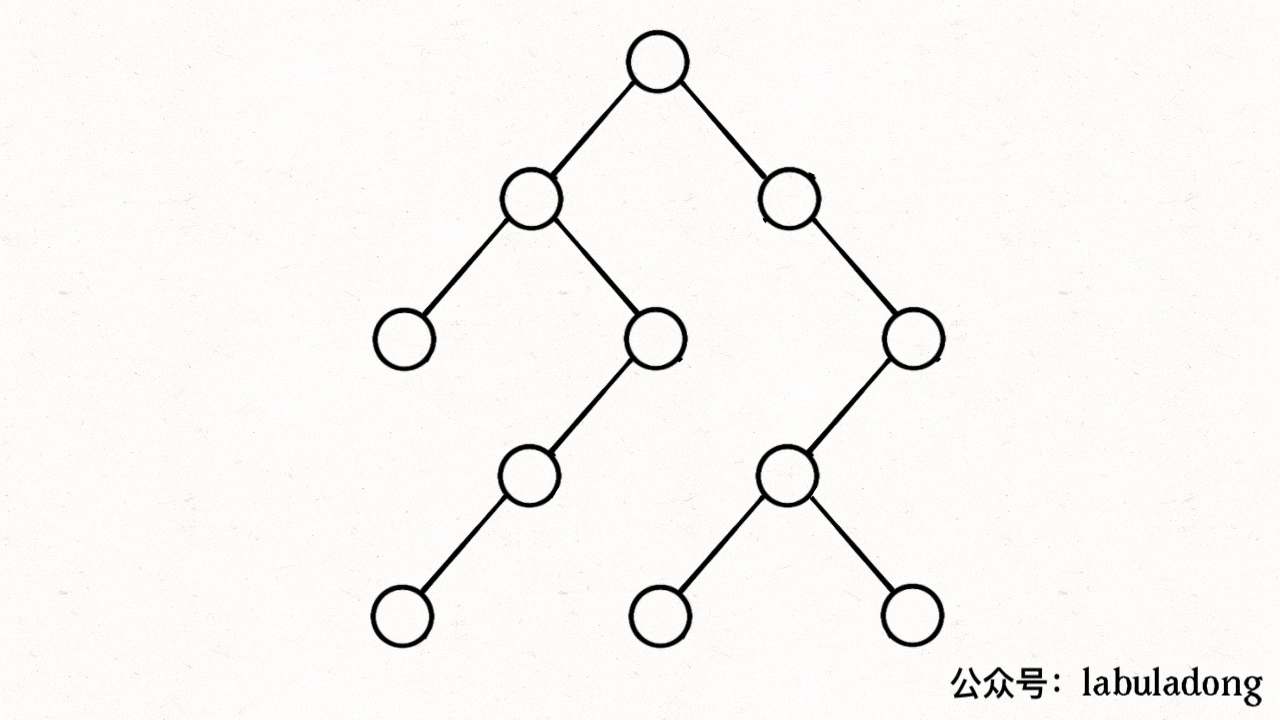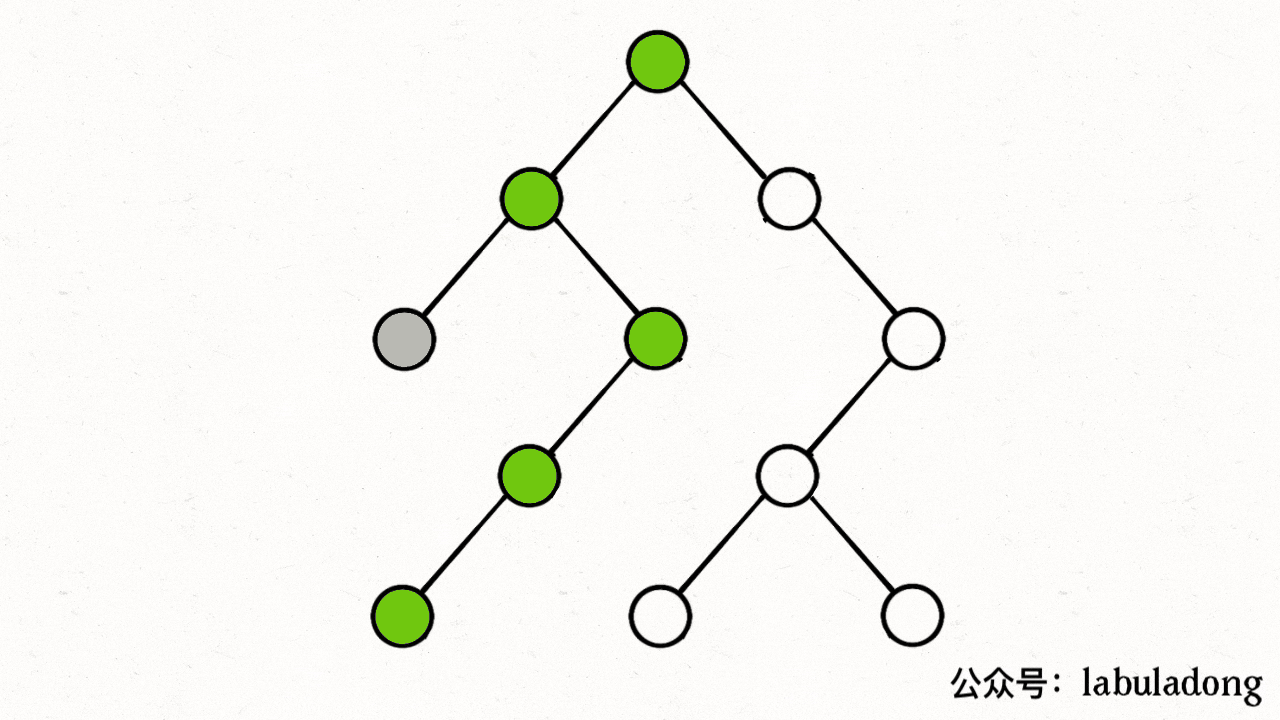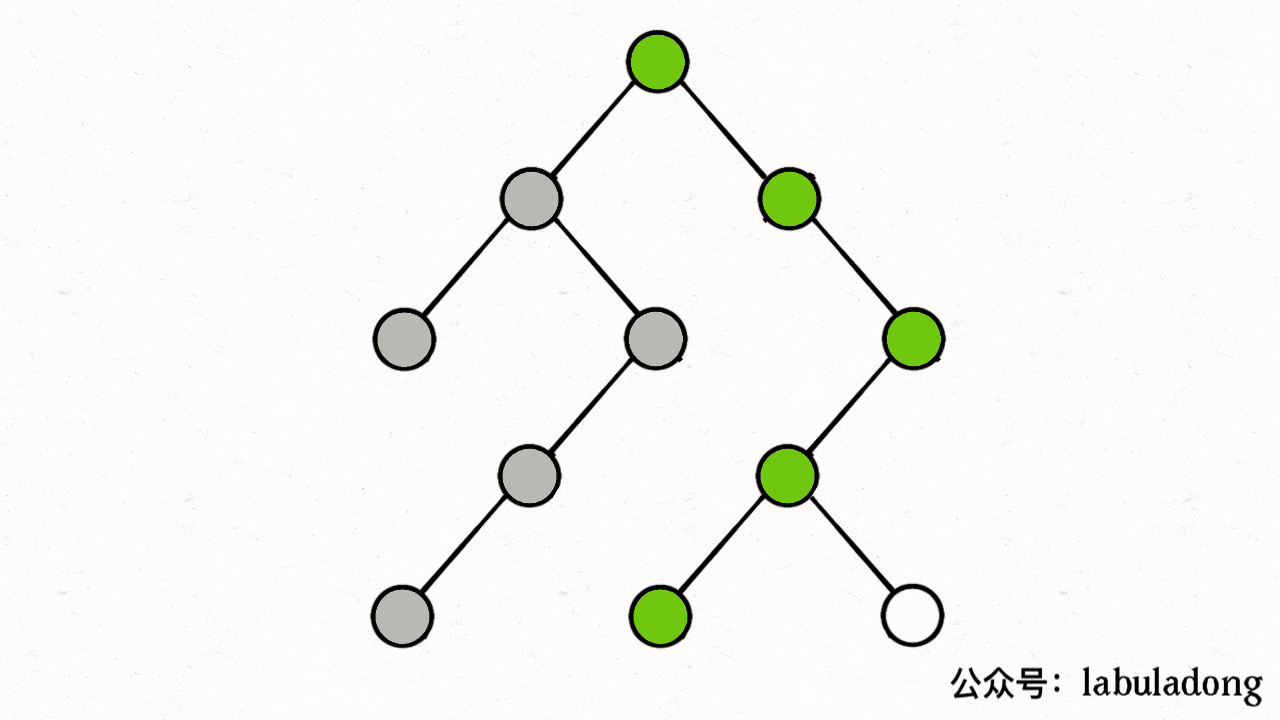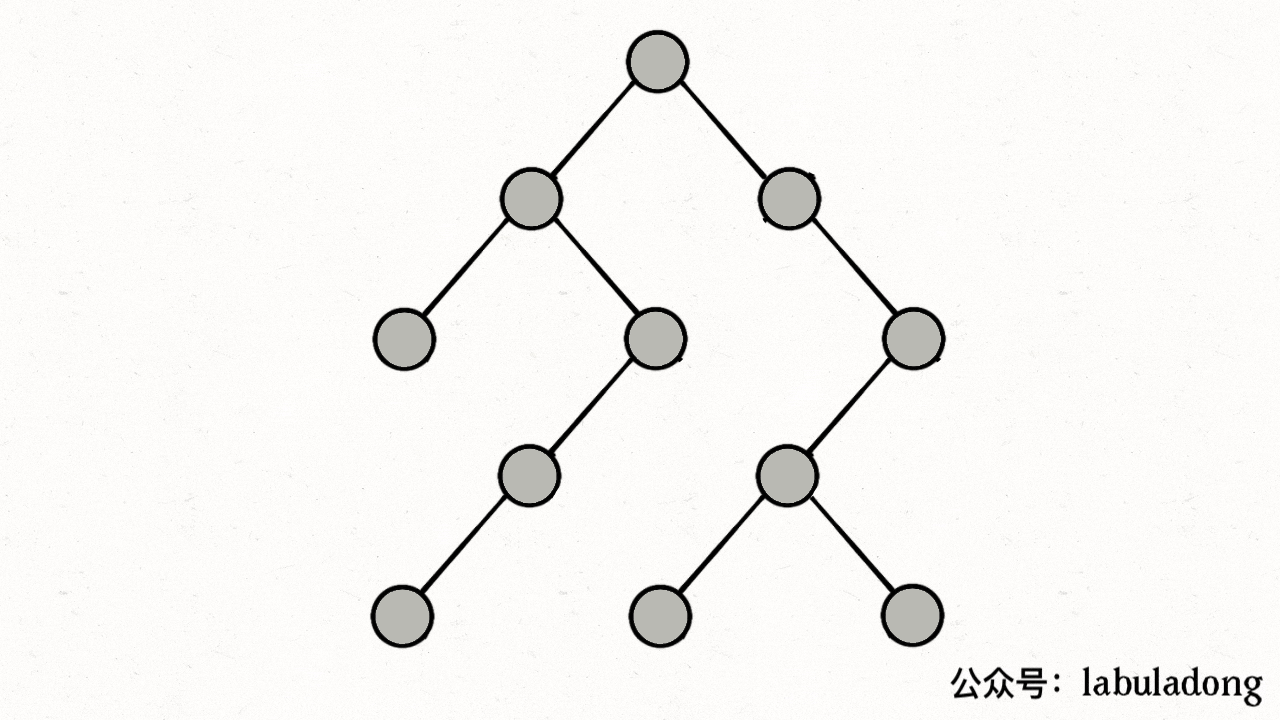
visited 中用灰色标记已经遍历过的节点,用onPath来表示正在遍历的节点
Dijkstra
Dijkstra
例题
这道题比较有意思的点在于其涉及到一个技巧:
从叶子结点BFS,越往深处,节点连接的点越多,最里面的点即为最小高度
举一反三:
这种套路题,找最近叶子节点就从根开始 BFS,找根节点的话就从叶子开始 BFS,记住这种处理方式就好了,一般不会有什么变体。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
| class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
int[] outDegree;
private void buildGraph(int n) {
outDegree = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
}
private void add(int from, int to) {
graph.get(from).add(to);
outDegree[from]++;
}
public List<Integer> findMinHeightTrees(int n, int[][] edges) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (n == 1) {
res.add(0);
return res;
}
buildGraph(n);
for (int i = 0; i < edges.length; i++) {
add(edges[i][0], edges[i][1]);
add(edges[i][1], edges[i][0]);
}
Deque<Integer> dq = new ArrayDeque<>();
for (int i = 0; i < outDegree.length; i++) {
if (outDegree[i] == 1) dq.addLast(i);
}
while (!dq.isEmpty()) {
int size = dq.size();
res = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
int cur = dq.pollFirst();
res.add(cur);
List<Integer> neighbors = graph.get(cur);
for (int neighbor : neighbors) {
outDegree[neighbor]--;
if (outDegree[neighbor] == 1) dq.addLast(neighbor);
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
|
建表:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| private void buildGraph(int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
}
private void add(int from, int to) {
graph.get(from).add(to);
}
|
从边出发,水往高处流
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
| class Solution {
int[] dx = new int[] {-1, 0, 0, 1};
int[] dy = new int[] {0, -1, 1, 0};
int[][] graph;
int m, n;
boolean[][] visited;
public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] heights) {
graph = heights;
m = heights.length;
n = heights[0].length;
Deque<int[]> dqPacific = new ArrayDeque<>();
Deque<int[]> dqAtlantic = new ArrayDeque<>();
boolean[][] flushSucceedPacific = new boolean[m][n];
boolean[][] flushSucceedAtlantic = new boolean[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (i == 0 || j == 0) {
dqPacific.add(new int[]{i, j});
flushSucceedPacific[i][j] = true;
}
if (i == m - 1 || j == n - 1) {
dqAtlantic.add(new int[] {i, j});
flushSucceedAtlantic[i][j] = true;
}
}
}
visited = new boolean[m][n];
bfs(dqPacific, flushSucceedPacific);
visited = new boolean[m][n];
bfs(dqAtlantic, flushSucceedAtlantic);
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (flushSucceedPacific[i][j] && flushSucceedAtlantic[i][j]) {
List<Integer> dir = new ArrayList<>();
dir.add(i);
dir.add(j);
ret.add(dir);
}
}
}
return ret;
}
private void bfs(Deque<int[]> dq, boolean[][] res) {
while (!dq.isEmpty()) {
int size = dq.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
int[] cur = dq.pollFirst();
int x = cur[0], y = cur[1];
int curHeight = graph[x][y];
for (int dir = 0; dir < 4; dir++) {
int newX = x + dx[dir], newY = y + dy[dir];
if (newX < 0 || newX >= m || newY < 0 || newY >= n) continue;
if (visited[newX][newY]) continue;
int newHeight = graph[newX][newY];
if (curHeight > newHeight) continue;
dq.addLast(new int[] {newX, newY});
visited[newX][newY] = true;
res[newX][newY] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
|
这是一道数学取巧题:
由于范围:
0 <= |x| + |y| <= 300
因此我们得知:
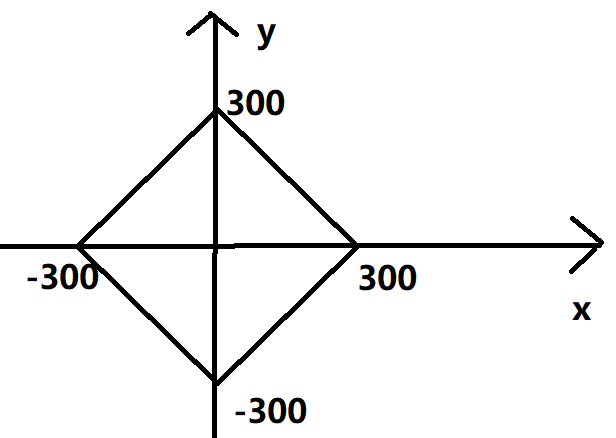
转换一下使得其适合从0开始的索引:
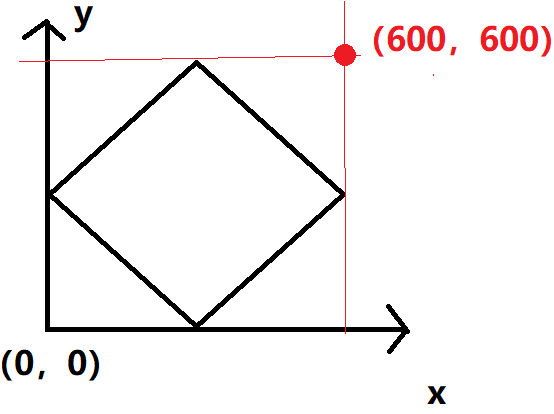
同时,为了避免目标(x,y)刚好在边界,我们往外再扩大成最右上角为 (666,666) 这是由于 我们 要的是 移动次数 所以不需要想坐标转换
直接贴一个别人的做法:
K.L.B 解法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
| class Solution {
int[][] dirs = new int[][]{
{1, 2}, {2, 1}, {2, -1}, {1, -2}, {-1, -2}, {-2, -1}, {-2, 1}, {-1, 2}
};
public int minKnightMoves(int x, int y) {
int dist = 0;
int abs = getMhdDist(0, 0, x, y);
boolean[][] mark = new boolean[666][666];
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
Node curNode = new Node(0, 0, 0);
Node newNode = null;
mark[333][333] = true;
queue.add(curNode);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
curNode = queue.remove();
int curX = curNode.x;
int curY = curNode.y;
int curDist = curNode.dist;
if (curX == x && curY == y) {
return curDist;
}
int mhdist = getMhdDist(curX, curY, x, y);
for (int[] dir : dirs) {
int newX = curX + dir[0];
int newY = curY + dir[1];
int nextDist = curDist + 1;
if (mark[newX + 333][newY + 333]) {
continue;
}
if (mhdist > getMhdDist(newX, newY, x, y) || abs < 4) {
newNode = new Node(newX, newY, nextDist);
queue.add(newNode);
mark[newX + 333][newY + 333] = true;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
private int getMhdDist(int i, int j, int x, int y) {
return Math.abs(i - x) + Math.abs(j - y);
}
class Node {
int x;
int y;
public int dist;
public Node(int x, int y, int dist) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.dist = dist;
}
}
}
作者:K.L.B
链接:https:
|
这道题复杂在需要开一个额外的维度来储存当前剩余的可以清空障碍的操作数量。不过剩下的就都是BFS了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| class Solution {
int[] dx = new int[]{-1, 0, 0, 1};
int[] dy = new int[]{0, -1, 1, 0};
public int shortestPath(int[][] grid, int k) {
Deque<int[]> dq = new ArrayDeque<>();
dq.add(new int[]{0, 0, k});
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
if ((m == 1) && (n == 1)) {
return 0;
}
int step = -1;
k = Math.min(k, m + n - 3);
boolean[][][] visited = new boolean[m][n][k + 1];
visited[0][0][k] = true;
if (k >= m + n - 3){
return m + n - 2;
}
while (!dq.isEmpty()) {
int size = dq.size();
step++;
while (size-- > 0) {
int[] cur = dq.pollFirst();
int x = cur[0], y = cur[1], kleft = cur[2];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int newX = x + dx[i];
int newY = y + dy[i];
if (x == m - 1 && y == n - 1) {
return step;
}
if (newX >= 0 && newX < m && newY >= 0 && newY < n && !visited[newX][newY][kleft]) {
if (grid[newX][newY] == 1 && kleft > 0) {
visited[newX][newY][kleft - 1] = true;
dq.addLast(new int[]{newX, newY, kleft - 1});
} else if (grid[newX][newY] == 0){
visited[newX][newY][kleft] = true;
dq.addLast(new int[]{newX, newY, kleft});
}
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
|