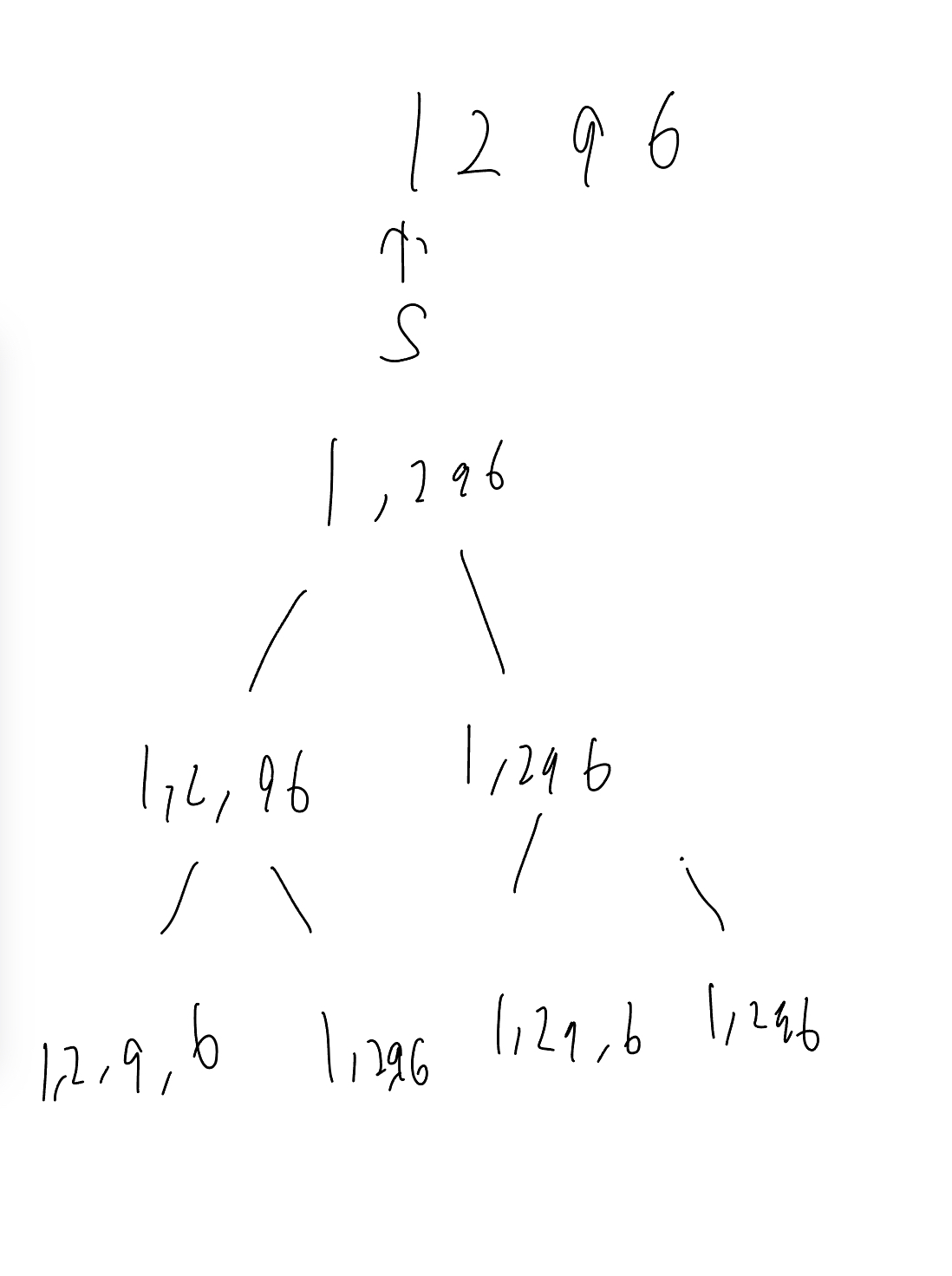二叉树 暂略,已经练习很多了
见 二叉树 中包含所有二叉树
回溯
回溯有一个增量构造答案的过程,这个过程通常使用递归来实现。选 “a”, “b”, “c” 选 “ad” …
递归: 考虑好边界条件以及和非边界条件写对即可。剩下交给数学归纳法
回溯/动归三问:-> 主要是为了写对 边界条件以及和非边界条件
当前操作是什么?
子问题是什么?
下一个子问题是什么?
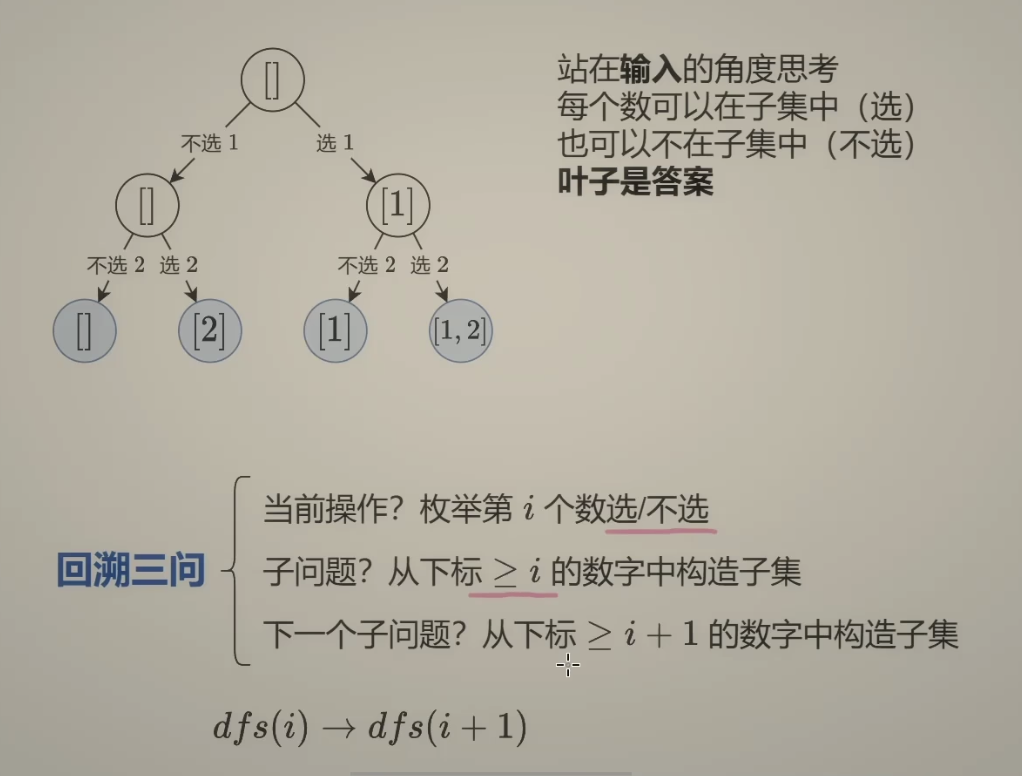
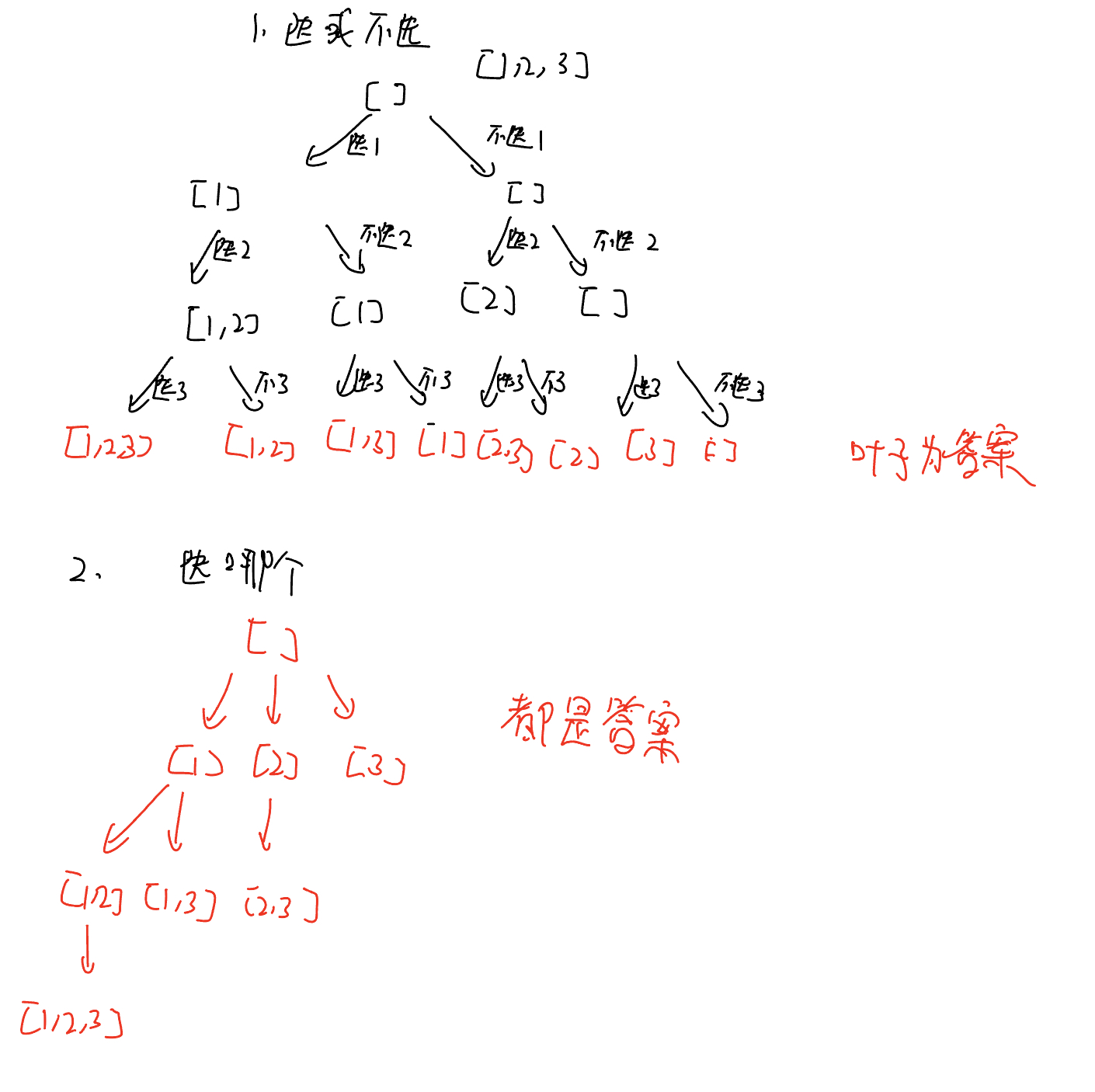
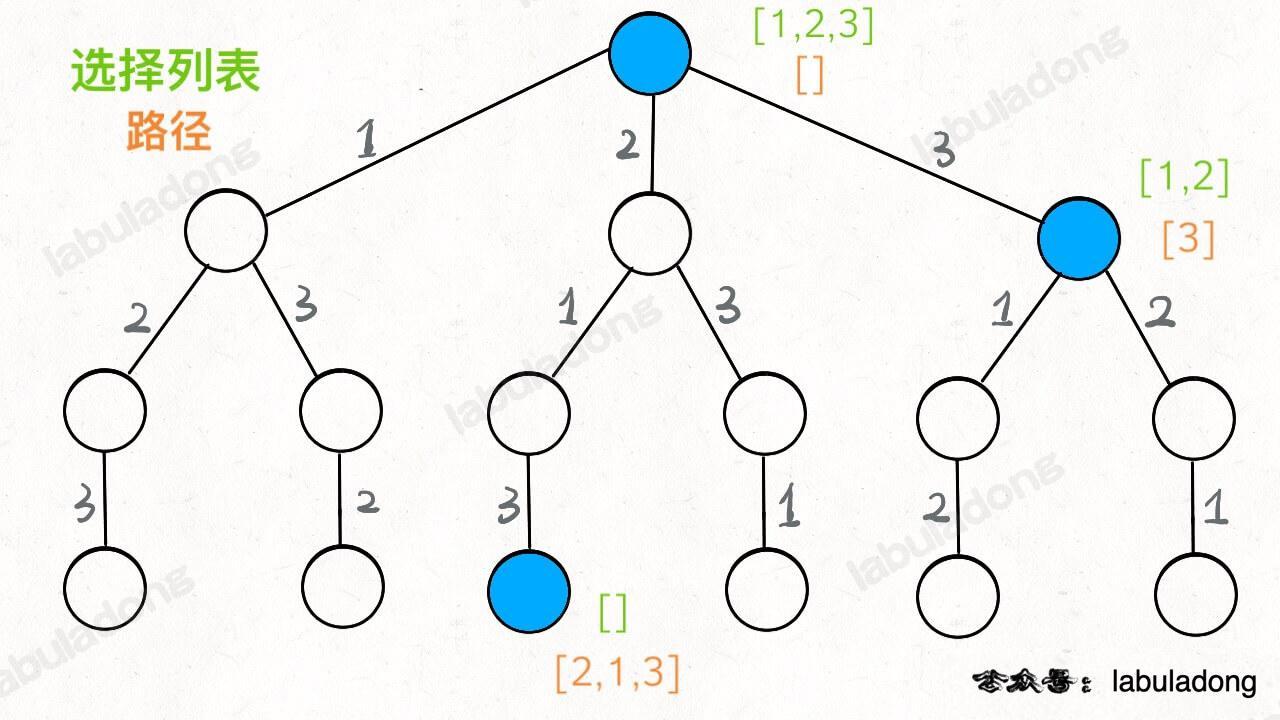
子集型 思路 可以有两种思路:
站在输入的角度:
枚举第 i 个元素 你是选/不选
ps: 01背包与此相似
每个数都可以在子集中,也可以不在子集中
此时:叶子结点是答案
回溯三问:
当前操作
枚举第 i 个数选/不选
子问题
从下标 >= i 的数字中构造子集
下一个子问题
从下标 >= i + 1的数字中构造子集
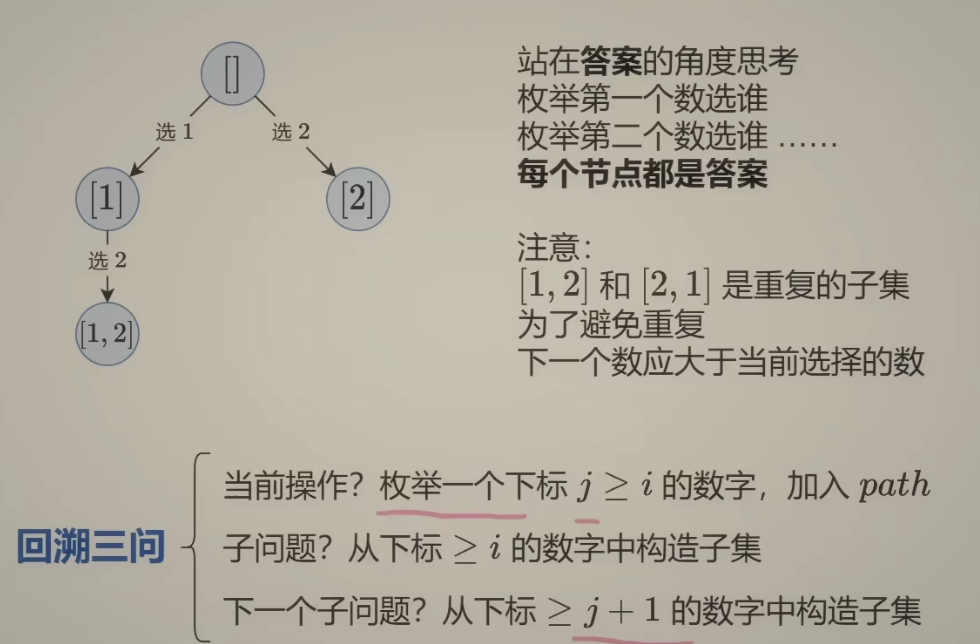
站在答案 角度:
枚举第一个数选择谁,第二个数选择谁,
此时:每个节点都是答案
回溯三问:
当前操作
枚举答案的第一个数选什么第二个数选什么…
子问题
从下标 >= i 的数字中构造子集
下一个子问题
从下标 >= j + 1的数字中构造子集
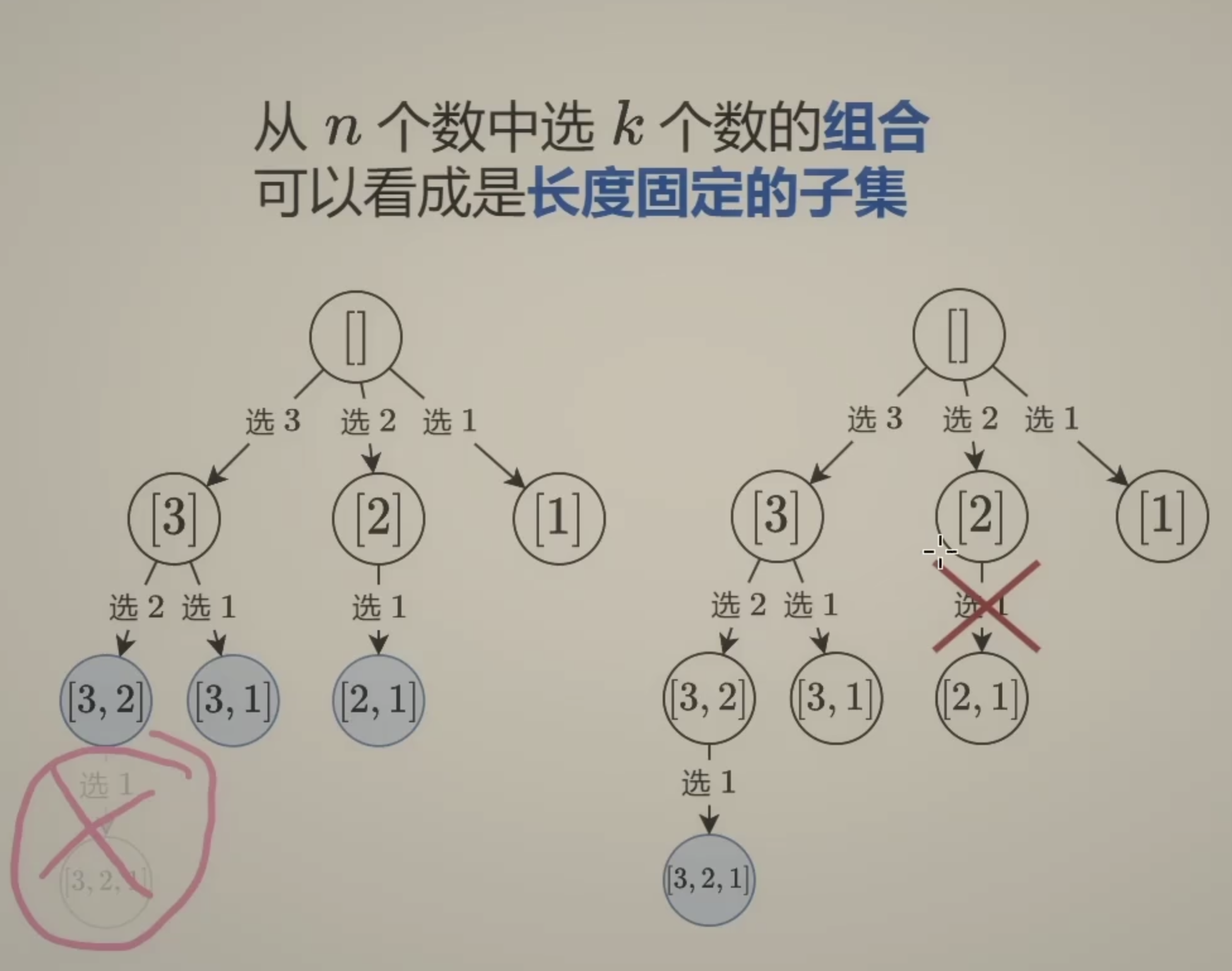
组合型 思路 子集 + 剪枝 = 组合型问题
下图(左选两个数,右选三个数)
为什么从大到小枚举呢?
假设我们需要选 3 个数,现在已经选了1个了,即 k = 3, m = 1; 我们还需要选择 d = k - m -> 3 - 1 = 2 个数
由于是从大到小枚举,那么我们如果 i < d; 即要选的数为[1,1] 也就是1的话那么是无论如何都没办法选出来两个数 k = 2 的(这是因为题目的范围是[1,n])所以从大到小会比较容易剪枝
正序枚举怎么做呢?
k - path.size() 是 我们还需要几个
我们要判断的就是还需要的能否被正确的提供,当前我们剩余的个数是 n - i + 1
因此如果需要的不能被满足,直接提前截止即可 if (k - path.size() > n - cur + 1) return;
总结 对于组合型和子集型回溯有两种思考路径:
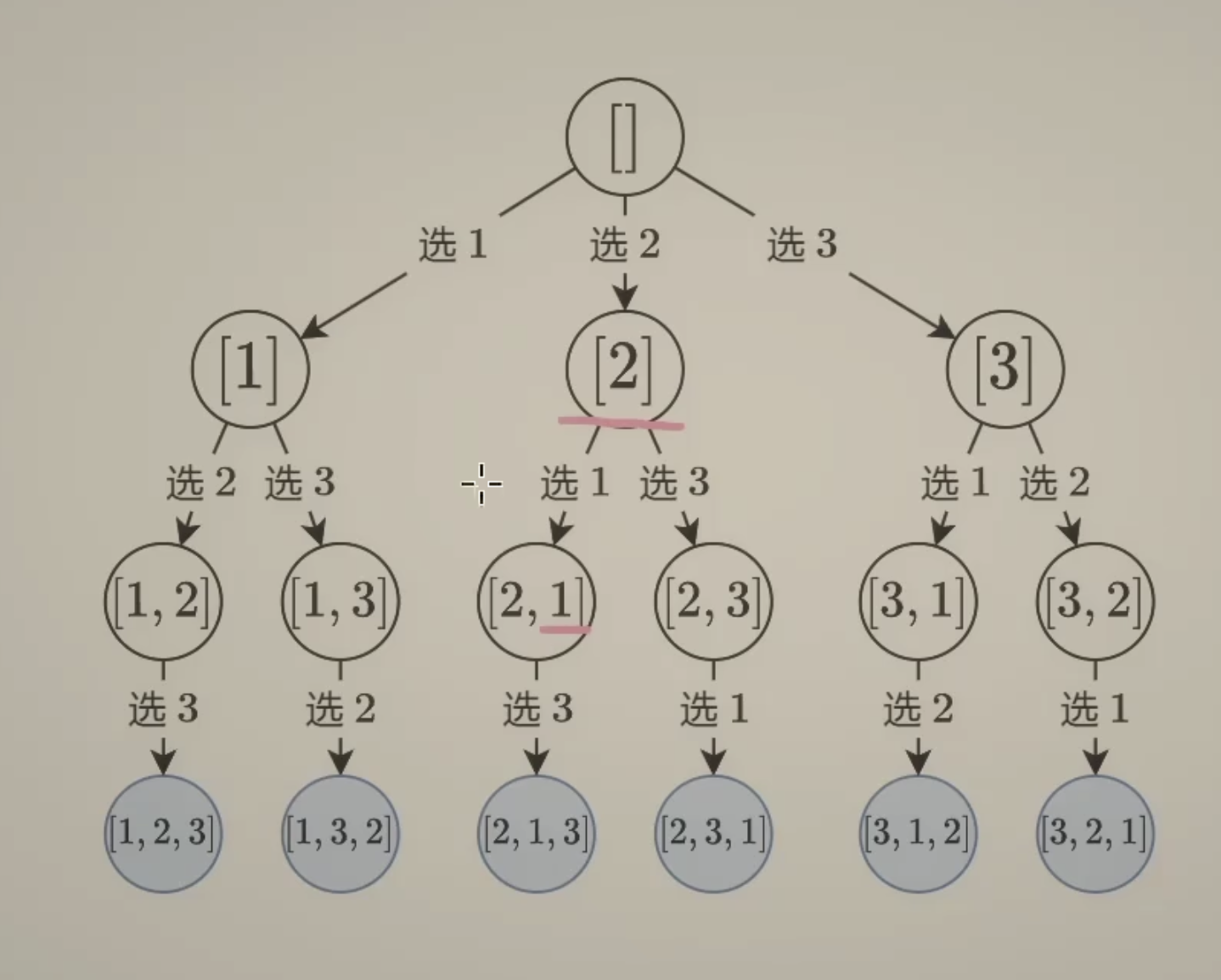
排列型
和组合的区别就在于[2, 1] 和 [1, 2]在组合中被认定为一种,但是排列中则是两种不同的
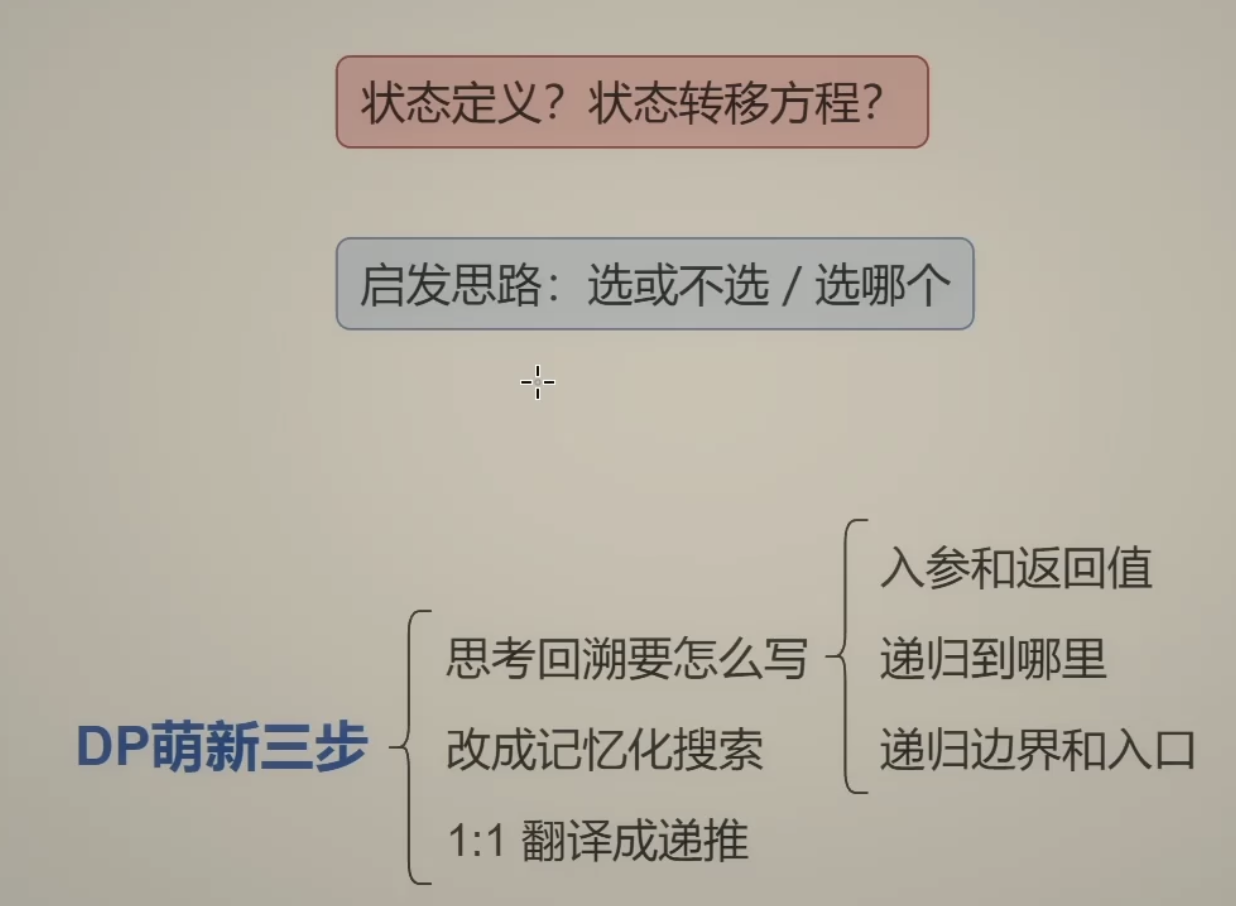
DP
主要还是
可以借用子集型回溯中的
选或不选 / 选哪个
从上至下 - 记忆化搜索
从下而上 - 递推
回溯例题 子集型 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 17. 电话号码的字母组合 https://leetcode.cn/problems/letter-combinations-of-a-phone-number/solutions/2059416/hui-su-bu-hui-xie-tao-lu-zai-ci-pythonja-3orv/ 78. 子集 https://leetcode.cn/problems/subsets/solutions/2059409/hui-su-bu-hui-xie-tao-lu-zai-ci-pythonja-8tkl/ 131. 分割回文串 https://leetcode.cn/problems/palindrome-partitioning/solutions/2059414/hui-su-bu-hui-xie-tao-lu-zai-ci-pythonja-fues/ 784. 字母大小写全排列 https://leetcode.cn/problems/letter-case-permutation/ 1601. 最多可达成的换楼请求数目 https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-number-of-achievable-transfer-requests/ 2397. 被列覆盖的最多行数 https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-rows-covered-by-columns/ 306. 累加数 https://leetcode.cn/problems/additive-number/ 2698. 求一个整数的惩罚数 https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-the-punishment-number-of-an-integer/
组合型 1 2 3 4 77. 组合 https://leetcode.cn/problems/combinations/solutions/2071017/hui-su-bu-hui-xie-tao-lu-zai-ci-pythonja-65lh/ 216. 组合总和 III https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum-iii/solutions/2071013/hui-su-bu-hui-xie-tao-lu-zai-ci-pythonja-feme/ 22. 括号生成 https://leetcode.cn/problems/generate-parentheses/solutions/2071015/hui-su-bu-hui-xie-tao-lu-zai-ci-pythonja-wcdw/ 301. 删除无效的括号 https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-invalid-parentheses/
排列型 1 2 3 46. 全排列 https://leetcode.cn/problems/permutations/solutions/2079585/hui-su-bu-hui-xie-tao-lu-zai-ci-jing-que-6hrh/ 51. N 皇后 https://leetcode.cn/problems/n-queens/solutions/2079586/hui-su-tao-lu-miao-sha-nhuang-hou-shi-pi-mljv/ 52. N 皇后 II(直接用 51 题代码搞定)https://leetcode.cn/problems/n-queens-ii/solution/hui-su-miao-sha-nhuang-hou-yi-ge-shi-pin-l41
子集型: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 class Solution { String[] hm = new String [] { "" , "" , "abc" , "def" , "ghi" , "jkl" , "mno" , "pqrs" , "tuv" , "wxyz" }; int n; char [] digitCharArr; List<String> res = new ArrayList <>(); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); public List<String> letterCombinations (String digits) { digitCharArr = digits.toCharArray(); n = digitCharArr.length; backtrack(0 ); return res; } private void backtrack (int curIdx) { if (curIdx == n) { String innerRes = sb.toString(); if (innerRes.length() != 0 ) res.add(innerRes); return ; } int idx = digitCharArr[curIdx] - '0' ; for (int i = 0 ; i < hm[idx].length(); i++) { sb.append(hm[idx].charAt(i)); backtrack(curIdx + 1 ); sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1 ); } return ; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 class Solution { int [] nums; int n; List<List<Integer>> paths = new ArrayList <>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>(); public List<List<Integer>> subsets (int [] nums) { this .nums = nums; n = nums.length; if (n == 0 ) return paths; backtrackSelectOrNot(0 ); backtrackChooseFromEnumeration(0 ); return paths; } private void backtrackSelectOrNot (int curIdx) { if (curIdx == n) { paths.add(new LinkedList <>(path)); return ; } path.addLast(nums[curIdx]); backtrackSelectOrNot(curIdx + 1 ); path.removeLast(); backtrackSelectOrNot(curIdx + 1 ); return ; } private void backtrackChooseFromEnumeration (int curIdx) { paths.add(new LinkedList <>(path)); if (curIdx == n) return ; for (int innerIdx = curIdx; innerIdx < n; innerIdx++) { path.addLast(nums[innerIdx]); backtrackChooseFromEnumeration(innerIdx + 1 ); path.removeLast(); } return ; } }
选或不选:
每一次抉择(backtrackSelectOrNot function中)都只有两种选择,选或者不选,并且这种情况下只有叶子结点为答案,因此需要判断是否为叶子结点,如果是的话才加入答案中
枚举选哪个:
每一次枚举(backtrackChooseFromEnumeration中)都可以选择curIdx之后的数,且所有的节点都为答案,因此无需判断直接加入,只需要做好递归的边界即可
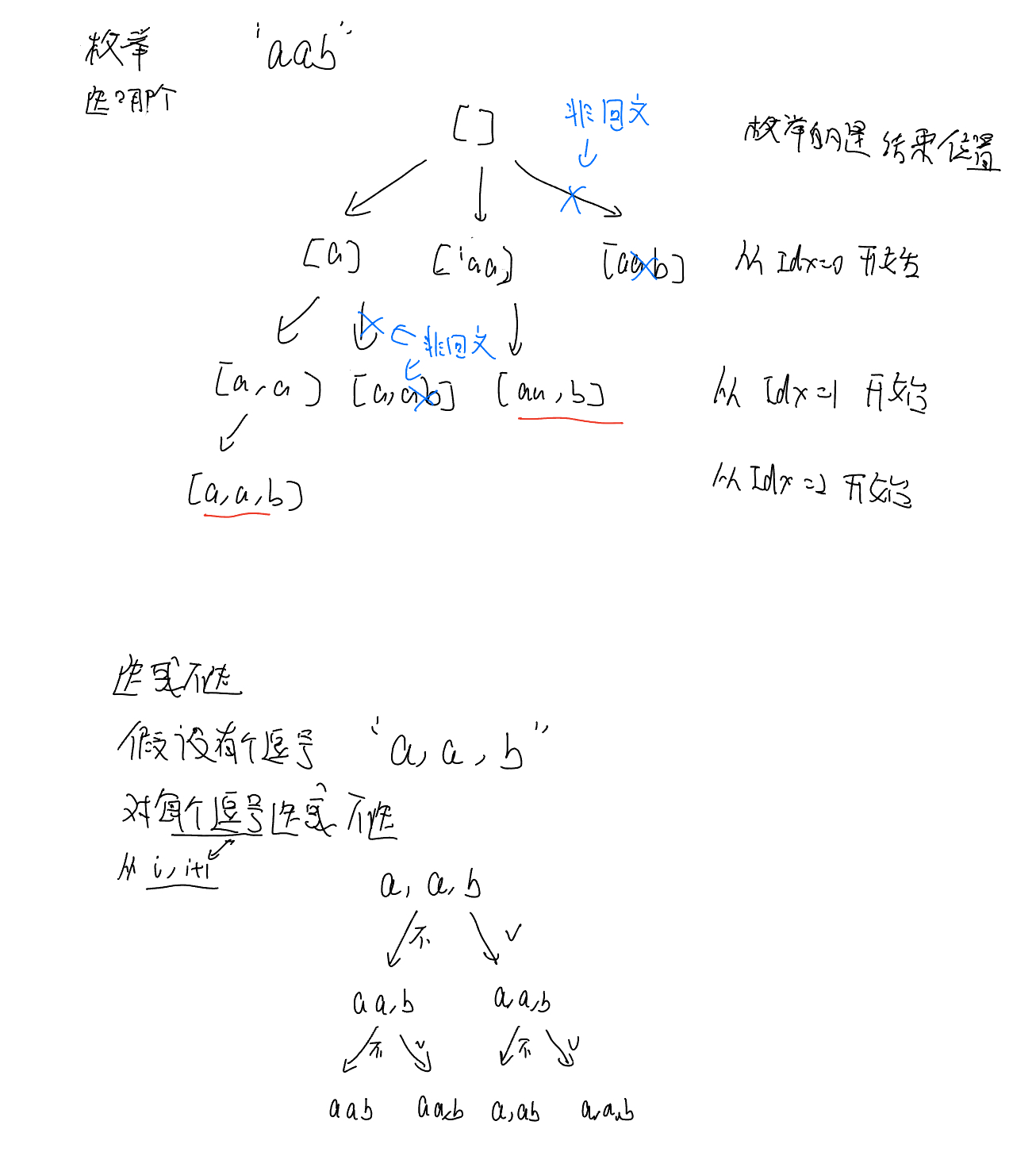
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 class Solution { int n; List<List<String>> paths = new ArrayList <>(); LinkedList<String> path = new LinkedList <>(); char [] sCharArr; String s; public List<List<String>> partition (String s) { n = s.length(); sCharArr = s.toCharArray(); this .s = s; backtrackSelectOrNot(0 , 0 ); return paths; } private void backtrackSelectOrNot (int start, int i) { if (start == n) { paths.add(new LinkedList <>(path)); return ; } if (i < n - 1 ) { backtrackSelectOrNot(start, i + 1 ); } if (isPalindrome(start, i)) { path.addLast(s.substring(start, i + 1 )); backtrackSelectOrNot(i + 1 , i + 1 ); path.removeLast(); } return ; } private void backtrackEnumerate (int start) { if (start == n) { paths.add(new LinkedList <>(path)); return ; } for (int i = start; i < n; i++) { if (isPalindrome(start, i)) { path.addLast(s.substring(start, i + 1 )); backtrackEnumerate(i + 1 ); path.removeLast(); } } return ; } private boolean isPalindrome (int left, int right) { while (left < right) { if (sCharArr[left] == sCharArr[right]) { left++; right--; } else { return false ; } } return true ; } }
两个难点:
决策树如何画
如何将char 小写变大写,大写变小写
问题1:
问题2:
Java碎碎念
char[idx] ^= 1 << 5
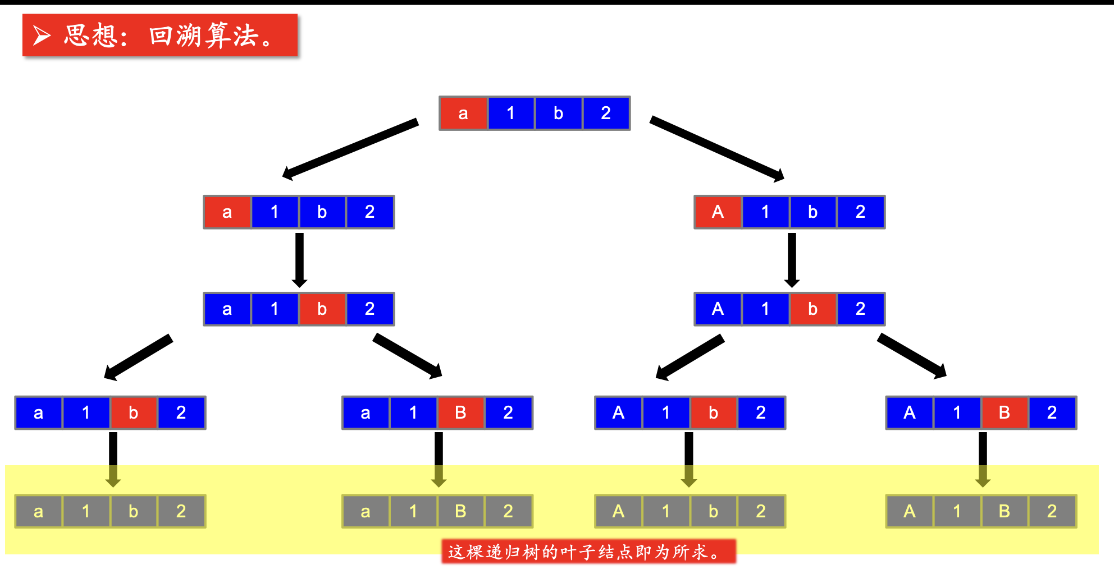
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution { int n; List<String> paths = new ArrayList <>(); char [] cArr; public List<String> letterCasePermutation (String s) { n = s.length(); cArr = s.toCharArray(); backtrack(0 ); return paths; } private void backtrack (int startIdx) { if (startIdx == n) { paths.add(new String (cArr)); return ; } if (Character.isDigit(cArr[startIdx])) { backtrack(startIdx + 1 ); return ; } cArr[startIdx] ^= 1 << 5 ; backtrack(startIdx + 1 ); cArr[startIdx] ^= 1 << 5 ; backtrack(startIdx + 1 ); return ; } }
这道题其实可以不用恢复现场,因为我们需要的是叶子结点;但是我们需要先处理 不转换当前char再处理转换当前char由于回溯发生在不转换,即没有变化,那也就不需要回溯现场了:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution { int n; List<String> paths = new ArrayList <>(); char [] cArr; public List<String> letterCasePermutation (String s) { n = s.length(); cArr = s.toCharArray(); backtrack(0 ); return paths; } private void backtrack (int startIdx) { if (startIdx == n) { paths.add(new String (cArr)); return ; } if (Character.isDigit(cArr[startIdx])) { backtrack(startIdx + 1 ); return ; } backtrack(startIdx + 1 ); cArr[startIdx] ^= 1 << 5 ; backtrack(startIdx + 1 ); return ; } }
这道题关键在于枚举列然后计算覆盖的行然后统计最大即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 class Solution { int max = -1 ; int m, n; int [][] matrix, matrixCopy; public int maximumRows (int [][] matrix, int numSelect) { m = matrix.length; n = matrix[0 ].length; this .matrix = matrix; matrixCopy = new int [m][]; for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { matrixCopy[i] = matrix[i].clone(); } backtrack(0 , numSelect); return max; } private void backtrack (int startIdx, int numSelect) { if (n - startIdx < numSelect) return ; if (numSelect == 0 ) { max = Math.max(max, countCovers()); return ; } for (int i = startIdx; i < n; i++) { for (int r = 0 ; r < m; r++) { matrix[r][i] = 0 ; } backtrack(i + 1 , numSelect - 1 ); for (int r = 0 ; r < m; r++) { matrix[r][i] = matrixCopy[r][i]; } } } private int countCovers () { int ret = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { int count = 0 ; for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { if (matrix[i][j] == 0 ) count++; } if (count == n) ret++; } return ret; } private void printMatrix () { for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { System.out.print(matrix[i][j] + " " ); } System.out.println(); } System.out.println(); } }
这道题自己的做法是枚举切割的起始点,能做但是比较复杂;
如果回溯返回boolean想要记录结果的话:
if (backtrack()) return true
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 import java.math.BigInteger;class Solution { int numSelected = 0 ; String num; int n; LinkedList<BigInteger> path = new LinkedList <>(); public boolean isAdditiveNumber (String num) { this .num = num; n = num.length(); return backtrack(0 ); } private boolean backtrack (int cutIdx) { if (cutIdx == n) { return path.size() >= 3 && check(path.get(path.size() - 3 ), path.get(path.size() - 2 ), path.get(path.size() - 1 )); } if (num.charAt(cutIdx) == '0' ) { if (path.size() >= 2 ) { if (check(path.get(path.size() - 2 ), path.get(path.size() - 1 ), BigInteger.ZERO)) { path.addLast(BigInteger.ZERO); if (backtrack(cutIdx + 1 )) return true ; path.removeLast(); } else { return false ; } } else { path.addLast(BigInteger.ZERO); if (backtrack(cutIdx + 1 )) return true ; path.removeLast(); } } else { for (int i = cutIdx; i < n; i++) { BigInteger current = new BigInteger (num.substring(cutIdx, i + 1 )); path.addLast(current); if (path.size() >= 3 && !check(path.get(path.size() - 3 ), path.get(path.size() - 2 ), current)) { path.removeLast(); continue ; } if (backtrack(i + 1 )) return true ; path.removeLast(); } } return false ; } private boolean check (BigInteger a, BigInteger b, BigInteger c) { BigInteger sum = a.add(b); return sum.equals(c); } }
三叶的解法 是枚举结束点
并且这里教了如何使用高精度加法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 class Solution { String num; int n; List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList <>(); public boolean isAdditiveNumber (String _num) { num = _num; n = num.length(); return dfs(0 ); } boolean dfs (int u) { int m = list.size(); if (u == n) return m >= 3 ; int max = num.charAt(u) == '0' ? u + 1 : n; List<Integer> cur = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = u; i < max; i++) { cur.add(0 , num.charAt(i) - '0' ); if (m < 2 || check(list.get(m - 2 ), list.get(m - 1 ), cur)) { list.add(cur); if (dfs(i + 1 )) return true ; list.remove(list.size() - 1 ); } } return false ; } boolean check (List<Integer> a, List<Integer> b, List<Integer> c) { List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList <>(); int t = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < a.size() || i < b.size(); i++) { if (i < a.size()) t += a.get(i); if (i < b.size()) t += b.get(i); ans.add(t % 10 ); t /= 10 ; } if (t > 0 ) ans.add(t); boolean ok = c.size() == ans.size(); for (int i = 0 ; i < c.size() && ok; i++) { if (c.get(i) != ans.get(i)) ok = false ; } return ok; } } 作者:宫水三叶 链接:https: 来源:力扣(LeetCode) 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
这道题非常有意思,可以用两个指针来做到选或不选的思路:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution { int sum = 0 ; public int punishmentNumber (int n) { int res = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { sum = 0 ; char [] square = Integer.toString(i * i).toCharArray(); if (backtrack(square, 0 , 0 , i)) { res += i * i; } } return res; } private boolean backtrack (char [] square, int start, int end, int i) { if (end == square.length) { return i == sum; } if (sum > i) return false ; if (end < square.length - 1 ) { if (backtrack(square, start, end + 1 , i)) return true ; } sum += sumUp(square, start, end); if (backtrack(square, end + 1 , end + 1 , i)) return true ; sum -= sumUp(square, start, end); return false ; } private int sumUp (char [] square, int start, int end) { int x = 0 ; for (int i = start; i <= end; i++){ x = x * 10 + square[i] - '0' ; } return x; } }
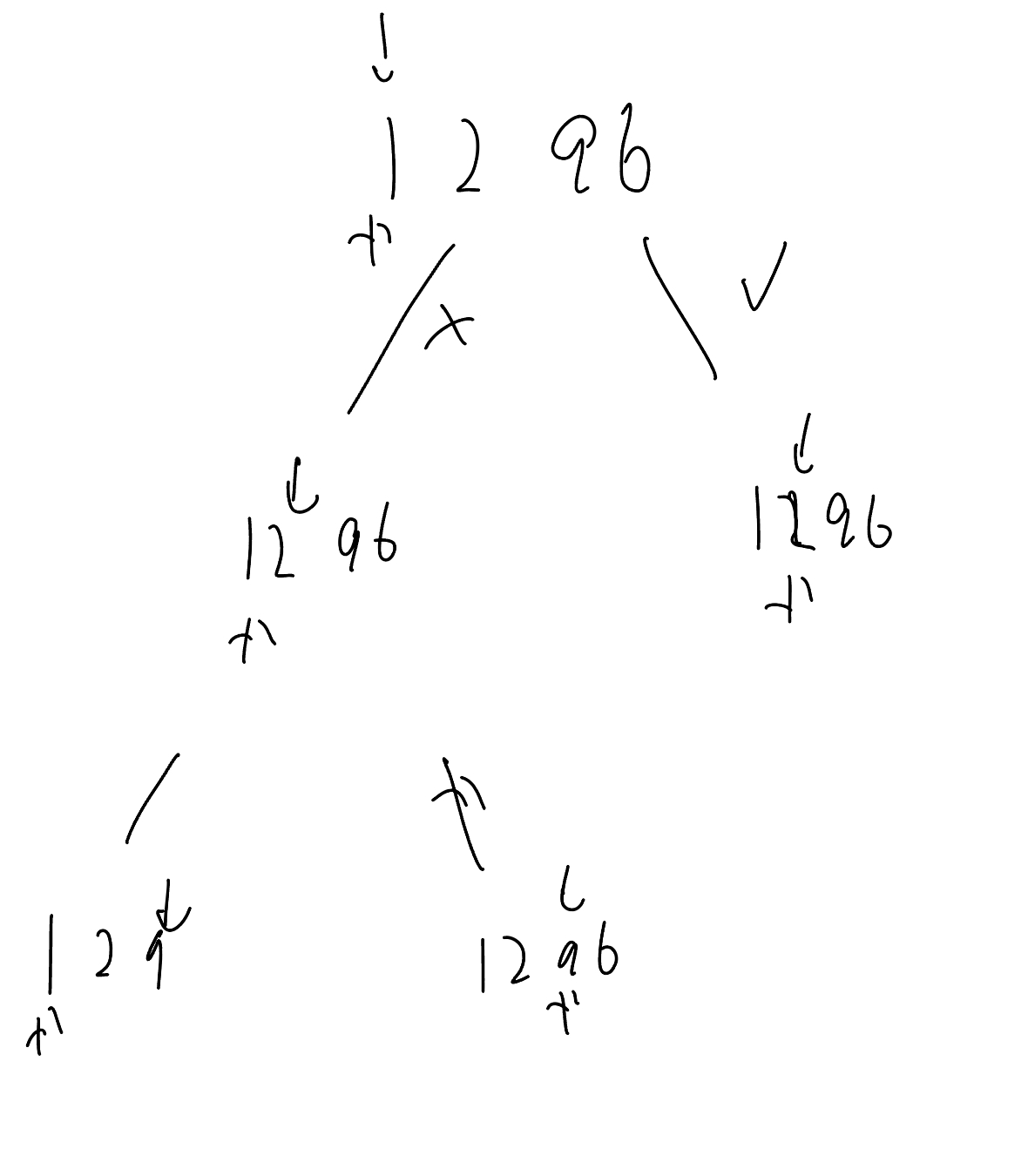
从答案的视角枚举
其实就是枚举逗号位置
在start = 0 时候 i尝试 0, 1, 2, 3 也就是[0,0],[0, 1], [0,2],[0,3] 即temp = 1, 12, 129, 1296 sum = 此时的 temp
在start = 1 时候 i尝试 1, 2, 3 也就是[1, 1], [1,2],[1,3] 即temp = 2, 29, 296; sum = start = 0 时候的temp + 此时的 temp
在start = 2 时候 i尝试 2, 3 也就是[2,2],[2,3] 即temp = 9, 96; sum = start = 0 时候的temp+ start = 1 时候的temp + 此时的 temp
在start = 3 时候 i尝试 3 也就是[3,3] 即temp = 6; sum = start = 0 时候的temp+ start = 1 时候的temp + start = 2 时候的temp+ 此时的 temp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution { int sum = 0 ; public int punishmentNumber (int n) { int res = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { sum = 0 ; char [] square = Integer.toString(i * i).toCharArray(); if (backtrackEnumeration(square, 0 , i)) { res += i * i; } } return res; } private boolean backtrackEnumeration (char [] square, int start, int target) { if (start == square.length) return target == sum; if (sum > target) return false ; int temp = 0 ; for (int i = start; i < square.length; i++) { temp = temp * 10 + square[i] - '0' ; sum = sum + temp; if (backtrackEnumeration(square, i + 1 , target)) { return true ; } sum = sum - temp; } return false ; } }
子集型总结 一般可以从选和不选以及枚举选哪个来做;
碰到需要选择切点的,类似于306, 以及2698题,我们可以先通过把一个数变成一个string或者char[]来进行枚举。
另外枚举状态下的回溯就是无非是当前层然后深入下一层然后碰到递归终点返回之后会继续尝试
其达成的效果就是当前层穷举,下一层穷举…
所以这就是所谓的递归不要管他是如何深入的。只要知道做了什么事,怎么出去,完成当前scope下的任务即可
组合型 无优化剪枝:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>(); List<List<Integer>> paths = new ArrayList <>(); int n, k; public List<List<Integer>> combine (int n, int k) { this .n = n; this .k = k; backtrack(1 ); return paths; } private void backtrack (int cur) { if (path.size() == k) { paths.add(new LinkedList <>(path)); return ; } for (int i = cur; i <= n; i++) { path.addLast(i); backtrack(i + 1 ); path.removeLast(); } } }
从大到小枚举剪枝:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>(); List<List<Integer>> paths = new ArrayList <>(); int n, k; public List<List<Integer>> combine (int n, int k) { this .n = n; this .k = k; backtrack(n); return paths; } private void backtrack (int cur) { if (path.size() == k) { paths.add(new LinkedList <>(path)); return ; } for (int i = cur; i >= 1 ; i--) { if (i < k - path.size()) return ; path.addLast(i); backtrack(i - 1 ); path.removeLast(); } } }
从小到大枚举
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>(); List<List<Integer>> paths = new ArrayList <>(); int n, k; public List<List<Integer>> combine (int n, int k) { this .n = n; this .k = k; backtrack(1 ); return paths; } private void backtrack (int cur) { if (k - path.size() > n - cur + 1 ) return ; if (path.size() == k) { paths.add(new LinkedList <>(path)); return ; } for (int i = cur; i <= n; i++) { path.addLast(i); backtrack(i + 1 ); path.removeLast(); } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 class Solution { LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>(); List<List<Integer>> paths = new ArrayList <>(); int k, n; public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3 (int k, int n) { this .k = k; this .n = n; backtrackSelectOrNot(1 ); return paths; } private void backtrackEnumeration (int start) { if (path.size() == k) { int sum = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < path.size(); i++) { sum += path.get(i); } if (sum == n) paths.add(new LinkedList <>(path)); return ; } for (int i = start; i <= 9 ; i++) { path.addLast(i); backtrackEnumeration(i + 1 ); path.removeLast(); } return ; } private void backtrackSelectOrNot (int cur) { if (cur > 9 ) { if (path.size() != k) return ; } if (path.size() == k) { int sum = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < path.size(); i++) { sum += path.get(i); } if (sum == n) paths.add(new LinkedList <>(path)); return ; } backtrackSelectOrNot(cur + 1 ); path.addLast(cur); backtrackSelectOrNot(cur + 1 ); path.removeLast(); return ; } }
依旧是使用了选和不选的操作:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution { LinkedList<Character> path = new LinkedList <>(); List<String> paths = new ArrayList <>(); int m; int n; public List<String> generateParenthesis (int n) { this .n = n; m = 2 * n; backtrackSelectOrNot(0 , 0 ); return paths; } private void backtrackSelectOrNot (int parenthesisSum, int leftParenthesisCount) { if (parenthesisSum == m) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); for (char c : path) { sb.append(c); } paths.add(sb.toString()); return ; } if (leftParenthesisCount < n) { path.addLast('(' ); backtrackSelectOrNot(parenthesisSum + 1 , leftParenthesisCount + 1 ); path.removeLast(); } if (parenthesisSum - leftParenthesisCount < leftParenthesisCount) { path.addLast(')' ); backtrackSelectOrNot(parenthesisSum + 1 , leftParenthesisCount); path.removeLast(); } return ; } }
需要注意的是这个树的构成是要计算左右可选的括号数量而不是盲目的选或者不选。
比如:我们一开始会选择左括号,当不选择左括号的时候(左括号数量满足数量),我们会去选择有括号,这时候是不选左括号的下分情况的选择右括号的情况:(右括号的数量 < 左括号的数量)
暴力的穷举每一个括号看是选择还是不选择
答案加入到数组里后从中选择最长的就是满足要求的,将最长的加入答案
另外判断一个字符串的括号是否合法的函数也很有意思,可以多学习一下, 思路是用代表左括号的指针移动,碰到左括号右移,右括号左移,如果left == 0证明合法,否则比如左括号的idx < 0则代表右括号>左括号数量,不合法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 class Solution { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); List<String> paths = new ArrayList <>(); String s; int n; public List<String> removeInvalidParentheses (String s) { this .s = s; n = s.length(); backtrack(0 ); return filterResult(); } private List<String> filterResult () { int maxLen = 0 ; for (String str : paths) { maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, str.length()); } HashSet<String> set = new HashSet <>(); for (String str : paths) { if (str.length() == maxLen) { set.add(str); } } return new LinkedList <>(set); } private void backtrack (int idx) { if (idx == n) { if (isValid(sb.toString())) { paths.add(sb.toString()); } return ; } char c = s.charAt(idx); if (c != '(' && c != ')' ) { sb.append(c); backtrack(idx + 1 ); sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1 ); } else { sb.append(c); backtrack(idx + 1 ); sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1 ); backtrack(idx + 1 ); } return ; } private boolean isValid (String sb) { int left = 0 ; for (char c : sb.toCharArray()) { if (c == '(' ) { left++; } else if (c == ')' ) { left--; if (left < 0 ) { return false ; } } } return left == 0 ; } }
排列型 代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution { LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>(); List<List<Integer>> paths = new ArrayList <>(); int [] nums; boolean [] numAppeared; int n; public List<List<Integer>> permute (int [] nums) { this .nums = nums; n = nums.length; numAppeared = new boolean [n]; backtrack(0 ); return paths; } private void backtrack (int idx) { System.out.println(idx + " " + path); if (idx == n) { paths.add(new LinkedList <>(path)); return ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { if (!numAppeared[i]) { numAppeared[i] = true ; path.addLast(nums[i]); backtrack(idx + 1 ); path.removeLast(); numAppeared[i] = false ; } } return ; } }
这里需要注意的有两个点:
backtrack中的for loop 是 i: [0, n) 因为我们每一次都要看从 0 开始的然后通过boolean[] 来判断是否加入答案
注意递归时候是 (idx + 1) 而不是 (i + 1)
idx应该表示的是当前的排列中已经放置了多少数字,或者说正在为哪个位置选择数字。然后选择的是 [0, n]
N皇后问题 这道题有两种思维方式,首先是 labuladong 的比较好理解的,其次是灵神 的通过抽屉原理证明的全排列
其方法核心大差不差,主要是在构造上
核心:枚举每一行上的皇后的全排列,在不冲突的前提下进行构造
labuladong版本:
整体比较长,每一次都需要判断左上和右上角是否冲突
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 class Solution { List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList <>(); public List<List<String>> solveNQueens (int n) { char [][] chessBoard = new char [n][n]; for (char [] chessRow : chessBoard) { Arrays.fill(chessRow, '.' ); } int curRow = 0 ; backtracking(chessBoard, curRow, n); return res; } private void backtracking (char [][] chessBoard, int curRow, int n) { if (curRow == n) { res.add(array2List(chessBoard)); return ; } for (int curCol = 0 ; curCol < n; curCol++) { if (isValid(chessBoard, curRow, curCol)) { chessBoard[curRow][curCol] = 'Q' ; backtracking(chessBoard, curRow + 1 , n); chessBoard[curRow][curCol] = '.' ; } } } private boolean isValid (char [][] chessBoard, int curRow, int curCol) { for (int r = 0 ; r < curRow; r++) { if (chessBoard[r][curCol] == 'Q' ) return false ; } for (int r = curRow - 1 , c = curCol - 1 ; r >= 0 && c >= 0 ; r--, c--) { if (chessBoard[r][c] == 'Q' ) return false ; } for (int r = curRow - 1 , c = curCol + 1 ; r >= 0 && c < chessBoard[0 ].length; r--, c++) { if (chessBoard[r][c] == 'Q' ) return false ; } return true ; } private List<String> array2List (char [][] chessBoard) { List<String> transformedArray = new ArrayList <>(); int r = chessBoard.length, c = chessBoard[0 ].length; for (char [] chars : chessBoard) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); for (int j = 0 ; j < c; j++) { sb.append(chars[j]); } transformedArray.add(sb.toString()); } return transformedArray; } }
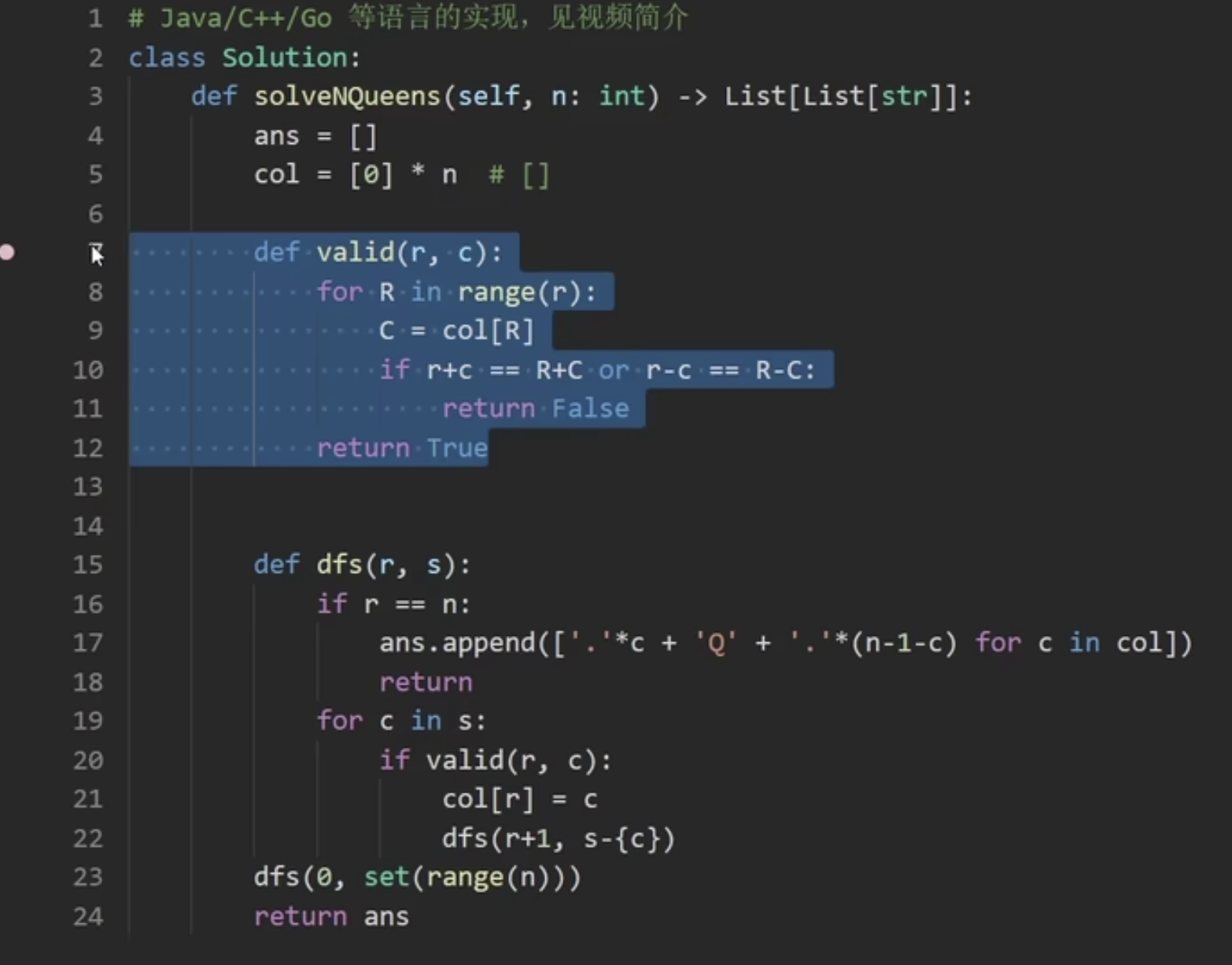
灵神的第一个版本也需要判断:
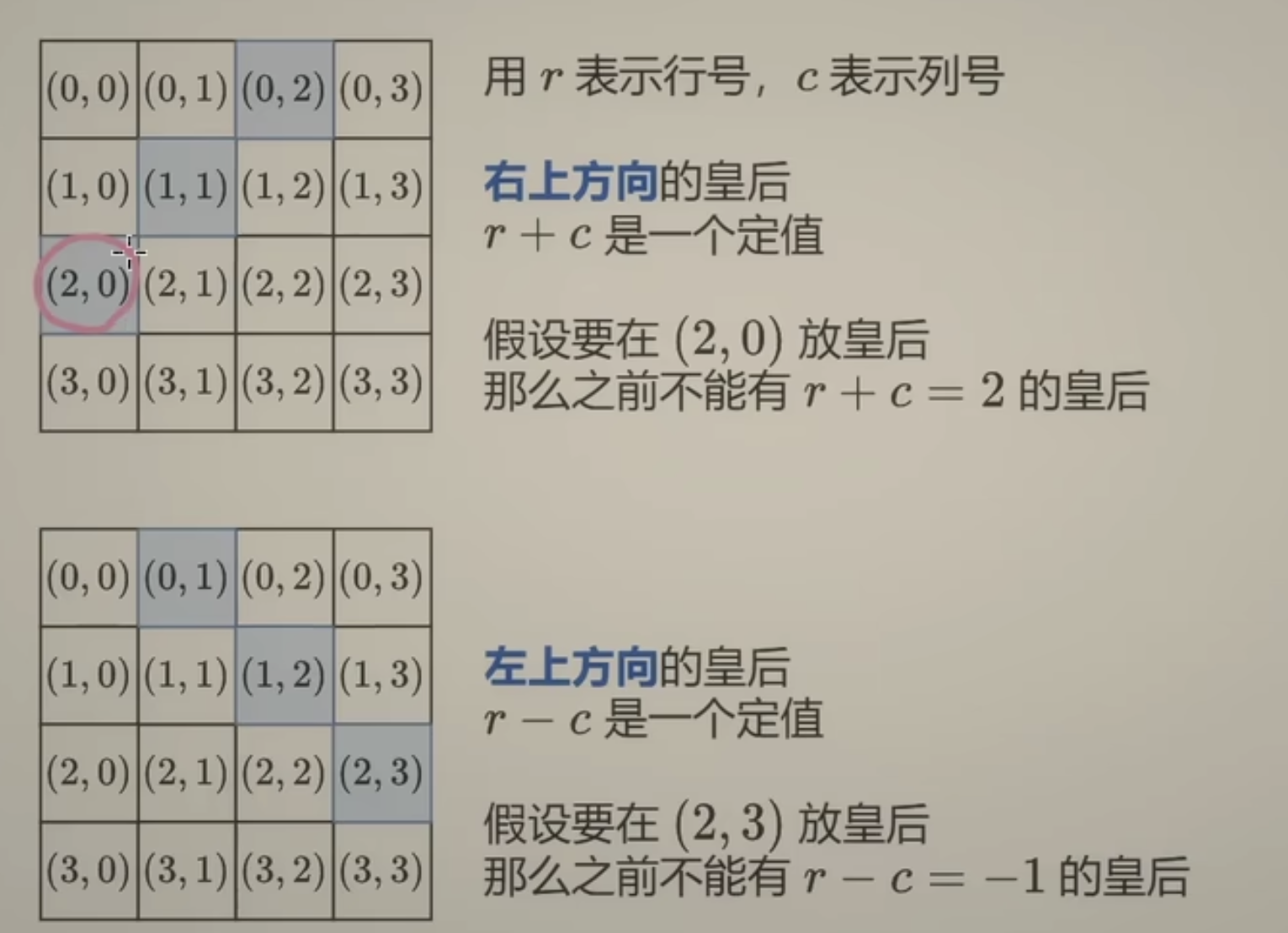
但是加入了一点数学证明:即右上方的 r + c == 当前的 r + c 左上方的 r - c == 当前的 r - c:
从而发现我们可以通过开辟两个boolean[]来看r + c是否之前出现过如果出现过就说明当前位置无法放置皇后因为会冲突
修改过后:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 class Solution { List<List<String>> paths = new ArrayList <>(); int [] col; boolean [] onPath, diagRPlusC, diagRMinusC; int m, n; public List<List<String>> solveNQueens (int n) { this .n = n; this .m = 2 * n - 1 ; col = new int [n]; onPath = new boolean [m]; diagRMinusC = new boolean [m]; diagRPlusC = new boolean [m]; backtrack(0 ); return paths; } private void backtrack (int r) { if (r == n) { List<String> board = new ArrayList <>(n); for (int c : col) { char [] row = new char [n]; Arrays.fill(row, '.' ); row[c] = 'Q' ; board.add(new String (row)); } paths.add(board); return ; } for (int c = 0 ; c < n; c++) { int rc = r - c + n - 1 ; if (!onPath[c] && !diagRPlusC[r + c] && !diagRMinusC[rc]) { col[r] = c; onPath[c] = diagRPlusC[r + c] = diagRMinusC[rc] = true ; backtrack(r + 1 ); onPath[c] = diagRPlusC[r + c] = diagRMinusC[rc] = false ; } } } }
只需要稍微更改下逻辑即可:这里我们返回计数而不是构造了一个答案
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution { int res; int [] col; boolean [] onPath, diagRPlusC, diagRMinusC; int m, n; public int totalNQueens (int n) { this .n = n; this .m = 2 * n - 1 ; col = new int [n]; onPath = new boolean [m]; diagRMinusC = new boolean [m]; diagRPlusC = new boolean [m]; backtrack(0 ); return res; } private void backtrack (int r) { if (r == n) { res++; return ; } for (int c = 0 ; c < n; c++) { int rc = r - c + n - 1 ; if (!onPath[c] && !diagRPlusC[r + c] && !diagRMinusC[rc]) { col[r] = c; onPath[c] = diagRPlusC[r + c] = diagRMinusC[rc] = true ; backtrack(r + 1 ); onPath[c] = diagRPlusC[r + c] = diagRMinusC[rc] = false ; } } } }
DP例题 DP 1 2 3 4 5 6 198. 打家劫舍 https://leetcode.cn/problems/house-robber/solutions/2102725/ru-he-xiang-chu-zhuang-tai-ding-yi-he-zh-1wt1/ 70. 爬楼梯 https://leetcode.cn/problems/climbing-stairs/ 746. 使用最小花费爬楼梯 https://leetcode.cn/problems/min-cost-climbing-stairs/ 2466. 统计构造好字符串的方案数 https://leetcode.cn/problems/count-ways-to-build-good-strings/ 213. 打家劫舍 II https://leetcode.cn/problems/house-robber-ii/ 213. 打家劫舍 II 题解 https://leetcode.cn/problems/house-robber-ii/solution/jian-ji-xie-fa-zhi-jie-diao-yong-198-ti-qhvri/
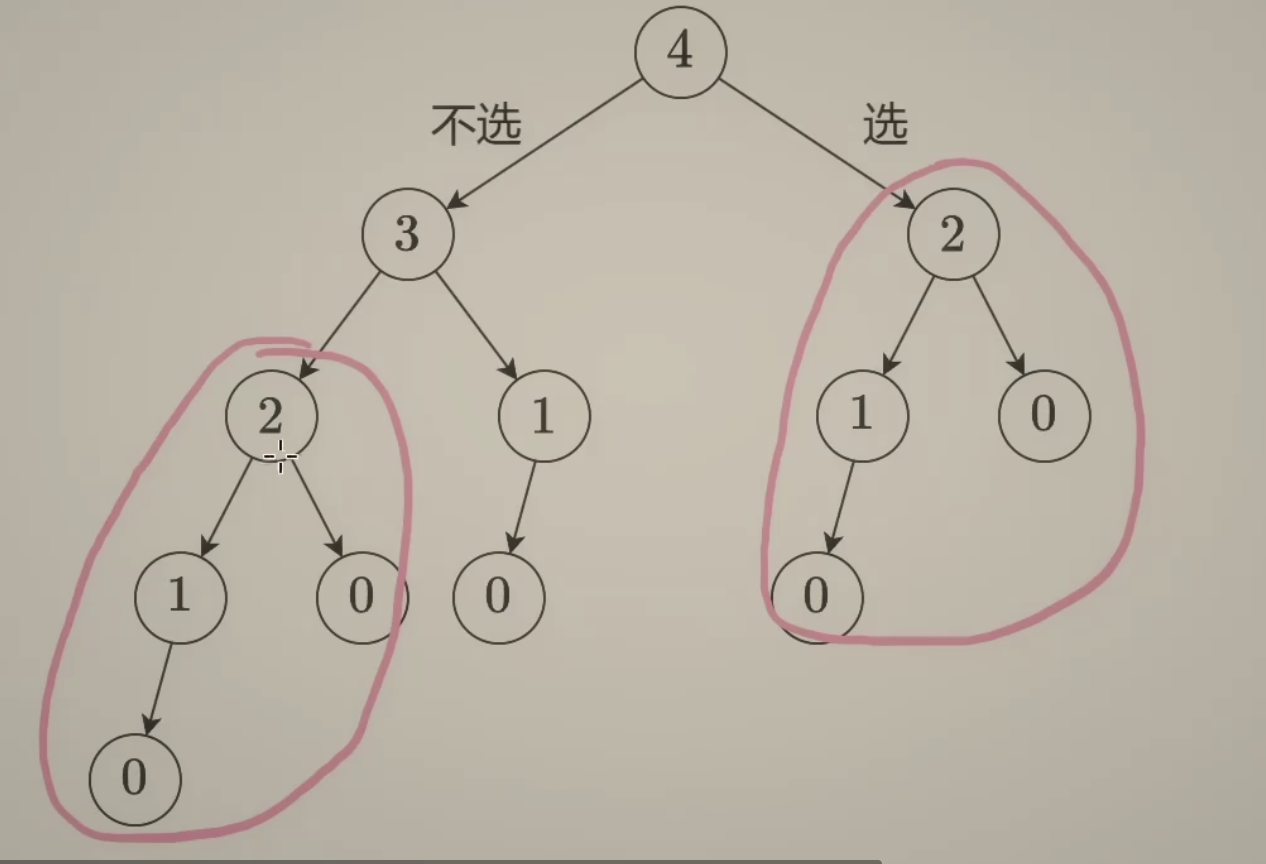
按照思路一步步来:
回溯怎么写:
当前操作:选或者不选当前这家偷
子问题和下一个子问题:
如果之前偷了,那就是从 n - 2开始
如果之前不偷,那就是从 n - 1开始
回溯代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { int [] nums; int n; public int rob (int [] nums) { this .nums = nums; n = nums.length; return backtrack(n - 1 ); } private int backtrack (int i) { if (i < 0 ) { return 0 ; } int res = Math.max(backtrack(i - 1 ), backtrack(i - 2 ) + nums[i]); return res; } }
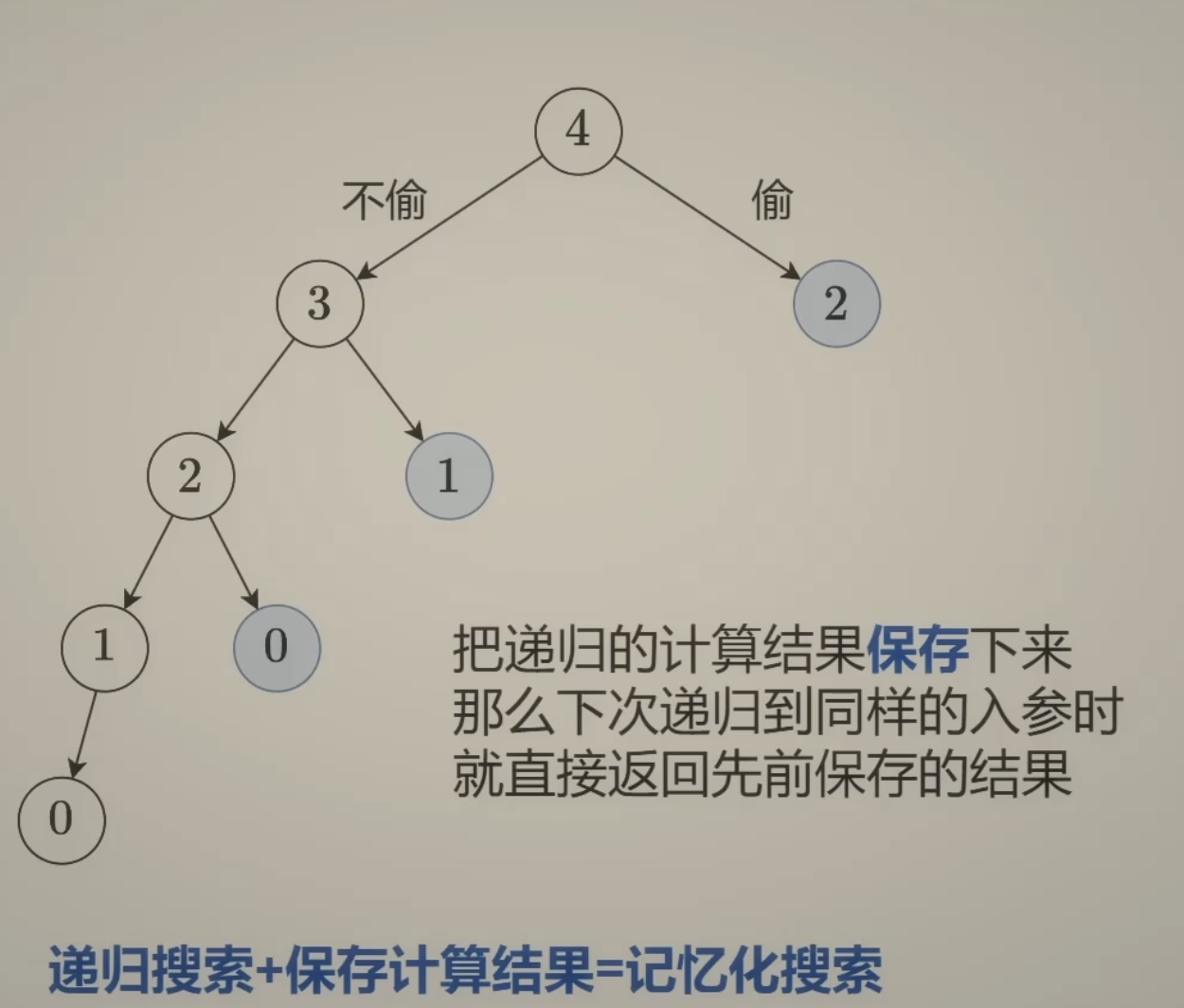
注意这里的回溯定义,返回了从 n - 1开始之前的打家劫舍的最大值
加入记忆化搜索:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { int [] nums; int n; int [] cache; public int rob (int [] nums) { this .nums = nums; n = nums.length; cache = new int [n]; Arrays.fill(cache, -1 ); return backtrack(n - 1 ); } private int backtrack (int i) { if (i < 0 ) { return 0 ; } if (cache[i] != -1 ) return cache[i]; int res = Math.max(backtrack(i - 1 ), backtrack(i - 2 ) + nums[i]); cache[i] = res; return res; } }
改造为递推
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public int rob (int [] nums) { int n = nums.length; int [] dp = new int [n + 2 ]; dp[n + 1 ] = 0 ; dp[n] = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { dp[i + 2 ] = Math.max(dp[i + 1 ], dp[i] + nums[i]); } return dp[n + 1 ]; } }
空间优化(由于 i + 2 只和i + 1 以及 i 有关)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public int rob (int [] nums) { int n = nums.length; int f = 0 ; int f1 = 0 ; int f0 = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { f = Math.max(f1, f0 + nums[i]); f0 = f1; f1 = f; } return f1; } }
由于现在是环形那么我们就是在原版的198中增加了一些条件限制:
如果选nums[0]进行偷窃,我们下一个偷的就从2开始;因为是环形,偷了第i = 0个意味着不能偷i = n - 1,也就是 偷n - 2
因此问题变成从nums[2] 到 nums[n−2] 的非环形版本,调用 198 题的代码解决
如果不选nums[0]进行偷窃,我们下一个偷的就从1开始;因为是环形,偷了第 i = 1个意味着不能偷i = n - 2,也就是 偷n - 1
因此问题变成从nums[1] 到 nums[n−1] 的非环形版本,调用 198 题的代码解决
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public int rob (int [] nums) { int n = nums.length; return Math.max(robFromLC198(nums, 2 , n - 2 ) + nums[0 ], robFromLC198(nums, 1 , n - 1 )); } public int robFromLC198 (int [] nums, int start, int end) { int n = nums.length; int f = 0 ; int f1 = 0 ; int f0 = 0 ; for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) { f = Math.max(f1, f0 + nums[i]); f0 = f1; f1 = f; } return f1; } }
这是一道树形DP:
这个考点叫树上最大独立集
最大独立集:从图中选出尽量多的点,是的这些点互不相邻;它的变形是最大化点权之和
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 class Solution { Map<TreeNode, Integer> memo = new HashMap <>(); public int rob (TreeNode root) { int [] res = dfs2(root); return Math.max(res[0 ], res[1 ]); } private int dfs (TreeNode node) { if (node == null ) return 0 ; if (memo.containsKey(node)) { return memo.get(node); } int rob_result = node.val + (node.left == null ? 0 : rob(node.left.left) + rob(node.left.right)) + (node.right == null ? 0 : rob(node.right.left) + rob(node.right.right)); int not_rob_result = rob(node.left) + rob(node.right); int result = Math.max(rob_result, not_rob_result); memo.put(node, result); return result; } private int [] dfs2(TreeNode node) { if (node == null ) return new int [] {0 , 0 }; int [] leftResult = dfs2(node.left); int [] rightResult = dfs2(node.right); int resRob = leftResult[0 ] + rightResult[0 ] + node.val; int resNotRob = Math.max(leftResult[0 ], leftResult[1 ]) + Math.max(rightResult[0 ], rightResult[1 ]); return new int [] {resNotRob, resRob}; } }
分成多个子问题,爬第n阶楼梯的方法数量,等于 2 部分之和
爬上 n−1 阶楼梯的方法数量。因为再爬1阶就能到第n阶
爬上 n−2 阶楼梯的方法数量,因为再爬2阶就能到第n阶
所以我们得到公式 dp[n]=dp[n−1]+dp[n−2]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public int climbStairs (int n) { if (n == 1 ) return 1 ; int f1 = 1 ; int f2 = 2 ; for (int i = 3 ; i <= n; i++) { int newF = f1 + f2; f1 = f2; f2 = newF; } return f2; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public int minCostClimbingStairs (int [] cost) { int [] dp = new int [cost.length + 1 ]; dp[0 ] = 0 ; dp[1 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 2 ; i < dp.length; i++) { dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i - 1 ] + cost[i - 1 ], dp[i - 2 ] + cost[i - 2 ]); } Arrays.stream(dp).forEach(e -> System.out.print(e + " " )); return dp[dp.length - 1 ]; } }
然后是基于dp数组的空间优化:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public int minCostClimbingStairs (int [] cost) { int dpi1 = 0 , dpi2 = 0 ; int minCost = 0 ; for (int i = 2 ; i < cost.length + 1 ; i++) { minCost = Math.min(dpi1 + cost[i - 1 ], dpi2 + cost[i - 2 ]); dpi2 = dpi1; dpi1 = minCost; } return minCost; } }
最后是这次写出来的版本:根本区别是我定义是到达这个位置的最小成本(初始化f0 = cost[0] f1 = cost[1])而之前的是初始化为0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution { public int minCostClimbingStairs (int [] cost) { int f0 = cost[0 ], f1 = cost[1 ]; for (int i = 2 ; i < cost.length; i++) { int newF = Math.min(f0, f1) + cost[i]; f0 = f1; f1 = newF; } return Math.min(f0, f1); } }
题目中:请你返回满足以上要求的 不同 好字符串数目。由于答案可能很大,请将结果对 109 + 7 取余 后返回。
范围比较大,就是大概率dp问题
这道题和 70 题类似思路是:
dp定义:dp[i] 是当前长度为i的字符串数目
所以答案是 dp[row] + … + dp[high]
状态转移:和 70 题类似:
70 是要么一次爬一级楼梯要么爬两级所以转移从 i - 1 以及 i - 2 得到
这道题是 转移从 zero 或者 one 得到
i - zero 为末尾加了 zero 个 零
i - one 为 末尾 加了 one 个 一
初始化 技巧:涉及到方案数我们可以列举Corner Case e.g.: 如果是空串,那么就是 f[0] = 1空串的字符串个数为1
取MOD
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { static final int MOD = (int ) 1e9 + 7 ; public int countGoodStrings (int low, int high, int zero, int one) { int [] dp = new int [high + 1 ]; dp[0 ] = 1 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= high; i++) { if (i >= zero) dp[i] = (dp[i] + dp[i - zero]) % MOD ; if (i >= one) dp[i] = (dp[i] + dp[i - one]) % MOD; } int ans = 0 ; for (int i = low; i <= high; i++) { ans = (ans + dp[i]) % MOD; } return ans; } }
例子:
1 2 输入:low = 3, high = 3, zero = 1, one = 1 输出:8
我们有dp数组:1 2 4 8
dp[1] = 2 (可以由1个1组成 或者 由1个0)dp[2] = 4 (10, 11,01,00)dp[3] = 8 (100,101,110,111,010,011,000,001)
所以就是每一次都将添加1或0后的形成的方案数+ 之前的结果转移得到
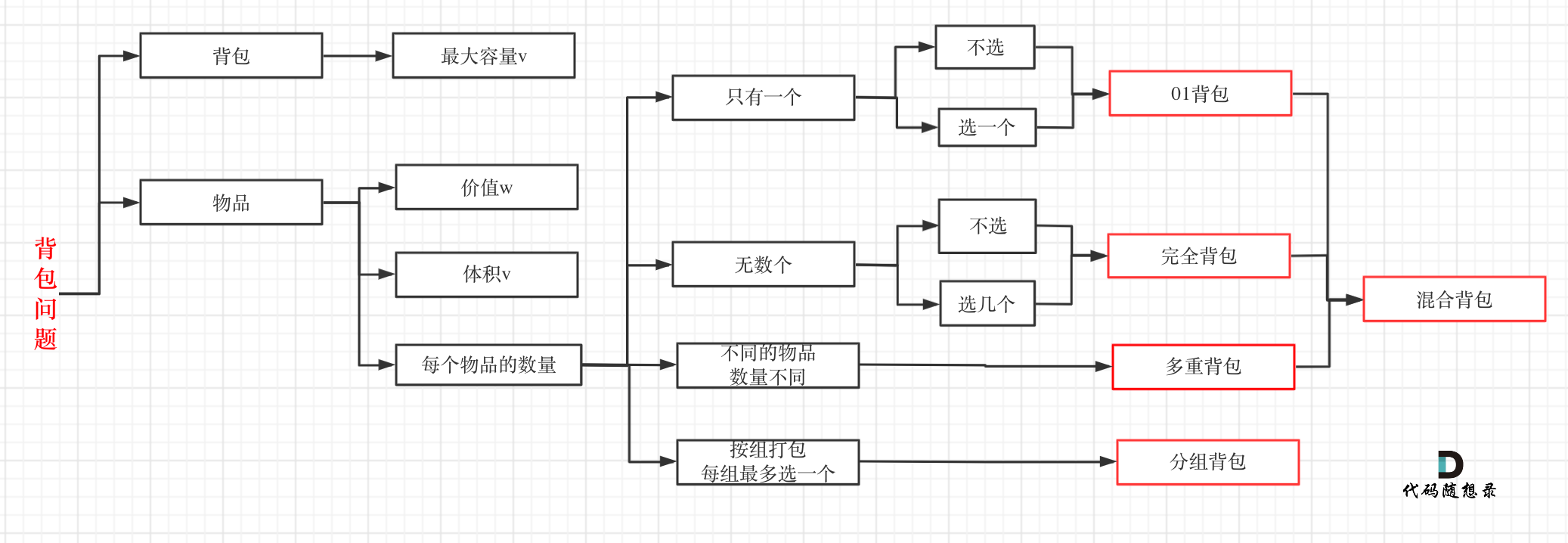
背包问题 0-1背包 和 完全背包 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 class Solution { int [] nums; int n; int [][] memo; public int findTargetSumWays (int [] nums, int target) { this .nums = nums; this .n = this .nums.length; int s = Arrays.stream(nums).sum(); int p = target + s; if (p % 2 != 0 || s < target || p < 0 ) return 0 ; p /= 2 ; int [] dp = new int [p + 1 ]; dp[0 ] = 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { int num = nums[i]; for (int j = p; j >= num; j--) { dp[j] = dp[j] + dp[j - num]; } } return dp[p]; } private int dp (int idx, int target) { if (idx < 0 ) { return target == 0 ? 1 : 0 ; } if (memo[idx][target] != -1 ) return memo[idx][target]; if (target < nums[idx]) { memo[idx][target] = dp(idx - 1 , target); return memo[idx][target]; } int tot = dp(idx - 1 , target) + dp(idx - 1 , target - nums[idx]); memo[idx][target] = tot; return tot; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 class Solution { int [] coins; int n; int [][] memo; public int coinChange (int [] coins, int amount) { this .n = coins.length; this .coins = coins; int [] dp = new int [amount + 1 ]; Arrays.fill(dp, Integer.MAX_VALUE / 2 ); dp[0 ] = 0 ; for (int coin : coins) { for (int capacity = coin; capacity <= amount; capacity++) { dp[capacity] = Math.min(dp[capacity], dp[capacity - coin] + 1 ); } } int ans = dp[amount]; return ans < Integer.MAX_VALUE / 2 ? ans : -1 ; } private int dp (int idx, int amount) { if (idx == n) { return amount == 0 ? 0 : Integer.MAX_VALUE / 2 ; } if (memo[idx][amount] != -1 ) return memo[idx][amount]; if (coins[idx] > amount) { memo[idx][amount] = dp(idx + 1 , amount); return memo[idx][amount]; } int res = Math.min(dp(idx + 1 , amount), dp(idx, amount - coins[idx]) + 1 ); memo[idx][amount] = res; return res; } }