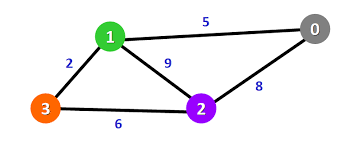
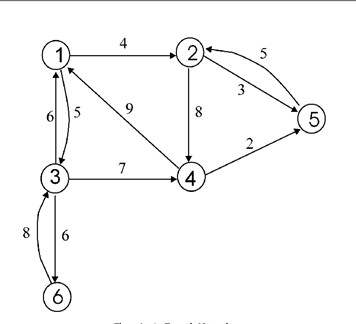
拓扑序列
- 一定得是有向图才(可能)会有拓扑序列
- 必须是由起点指向终点不能从后指向前
- 有向无环图一定存在拓扑序列
- DAG也被称为拓扑图
- 度数:
- 入度和出度
- 入度:有多少条边指向自己
- 出度:有多少条边出去

如何求拓扑序列
- 任何入度为0的都可以作为起点(当前最前面的位置)
- BFS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
Queue.add(所有入度为0的点)
while !queue.isEmpty() {
}
|
如果图中有环,那么一定会有点无法入队;反之,所有点都会在queue中
例子
拓扑排序其是一种有向无环图 (DAG) 的顶点排序方法,它将一个有向无环图的所有顶点排成一个线性序列,使得图中任意一条有向边的起点排在终点的前面
| 课程编号 |
课程名称 |
先修课程 |
| 1 |
高等数学 |
− |
| 2 |
程序设计基础 |
− |
| 3 |
离散数学 |
1, 2 |
| 4 |
数据结构 |
2, 3 |
| 5 |
高级语言程序设计 |
2 |
| 6 |
编译方法 |
4,5 |
| 7 |
操作系统 |
4,9 |
| 8 |
普通物理 |
1 |
| 9 |
计算机原理 |
8 |
这里使用了map建表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
| class Solution {
Map<String, LinkedList<String>> graph = new HashMap<>();
Map<String, Integer> inDegree = new HashMap<>();
int n;
public List<String> findAllRecipes(String[] recipes, List<List<String>> ingredients, String[] supplies) {
n = recipes.length;
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String recipe = recipes[i];
for (String ingredient : ingredients.get(i)) {
add(ingredient, recipe);
if (!inDegree.containsKey(ingredient)) {
inDegree.put(ingredient, 0);
}
updateInDegree(recipe);
}
if (!graph.containsKey(recipe)) {
graph.put(recipe, new LinkedList<>());
}
}
Deque<String> dq = new ArrayDeque<>();
for (String k : supplies) {
if (!inDegree.containsKey(k)) continue;
if (inDegree.get(k) == 0) {
dq.addLast(k);
}
}
while (!dq.isEmpty()) {
int size = dq.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
String curRecipe = dq.pollFirst();
List<String> neighbors = adj(curRecipe);
for (String neighbor : neighbors) {
int curIndegree = inDegree.get(neighbor) - 1;
inDegree.put(neighbor, curIndegree);
if (curIndegree == 0) {
dq.addLast(neighbor);
res.add(neighbor);
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
private void add(String from, String to) {
LinkedList<String> cur = graph.getOrDefault(from, new LinkedList<>());
cur.addLast(to);
graph.put(from, cur);
}
private void updateInDegree(String to) {
int cur = inDegree.getOrDefault(to, 0);
inDegree.put(to, cur + 1);
}
private List<String> adj(String cur) {
return graph.get(cur);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| class Solution {
int[] inDegree;
public int[] findOrder(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
inDegree = new int[numCourses];
Deque<Integer> dq = new ArrayDeque<>();
List<List<Integer>> graph = buildGraph(numCourses, prerequisites);
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
if (inDegree[i] == 0) dq.addLast(i);
}
int count = 0;
while (!dq.isEmpty()) {
int cur = dq.pollFirst();
path.add(cur);
count++;
List<Integer> neighbors = adj(graph, cur);
for (int next : neighbors) {
inDegree[next]--;
if (inDegree[next] == 0) dq.addLast(next);
}
}
if (count == numCourses) {
int[] res = new int[numCourses];
for (int i = 0; i < path.size(); i++) {
res[i] = path.get(i);
}
return res;
} else {
return new int[0];
}
}
private List<List<Integer>> buildGraph(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
List<List<Integer>> graph = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int i = 0; i < prerequisites.length; i++) {
int from = prerequisites[i][1], to = prerequisites[i][0];
add(graph, from, to);
inDegree[prerequisites[i][0]]++;
}
return graph;
}
private void add(List<List<Integer>> graph, int a, int b) {
graph.get(a).add(b);
}
private List<Integer> adj(List<List<Integer>> graph, int cur) {
return graph.get(cur);
}
}
|