链表 LinkedList
代码随想录-总汇 中包含链表的基础知识
题目:
707. 设计链表
边界非常多的题目,主要考虑如何更新链表节点的时候不要错误的更新。可以使用printHelper来帮助debug。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
| class MyLinkedList {
class Node {
Node prev;
Node next;
int val;
Node() {
}
Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
int count = 0;
Node head, tail;
public MyLinkedList() {
head = new Node();
tail = new Node();
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
public int get(int index) {
if (count <= index) return -1;
Node cur = head;
int curIdx = -1;
while (curIdx < index && cur != null) {
cur = cur.next;
curIdx++;
}
return curIdx == index ? cur.val : -1;
}
public void addAtHead(int val) {
Node cur = new Node(val);
Node headNext = head.next;
head.next = cur;
cur.prev = head;
cur.next = headNext;
headNext.prev = cur;
count++;
}
public void addAtTail(int val) {
Node cur = new Node(val);
Node tailPrev = tail.prev;
tail.prev = cur;
tailPrev.next = cur;
cur.prev = tailPrev;
cur.next = tail;
count++;
}
public void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
if (index > count) return;
Node cur = head;
int curIdx = -1;
while (curIdx < index && cur != null) {
cur = cur.next;
curIdx++;
}
if (index == curIdx) {
Node curPrev = cur.prev;
Node needAdd = new Node(val);
curPrev.next = needAdd;
needAdd.next = cur;
needAdd.prev = curPrev;
cur.prev = needAdd;
}
count++;
}
public void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
if (count <= index) {
return;
}
Node cur = head;
int curIdx = -1;
while (curIdx < index && cur != null) {
cur = cur.next;
curIdx++;
}
if (index == curIdx) {
Node curPrev = cur.prev;
curPrev.next = cur.next;
cur.next.prev = curPrev;
}
count--;
}
private void printHelper() {
Node cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val + "->");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
|
203. 移除链表元素
非常基础的删除链表中的元素题。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode();
dummyHead.next = head;
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode prev = dummyHead;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == val) {
prev.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
continue;
}
prev = prev.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
|
206. 反转链表
这道题主要在于如何使用递归:
递归实现反转链表常常用来考察递归思想,我这里就用纯递归来翻转链表。对于递归算法,最重要的就是明确递归函数的定义。具体来说,我们的 reverse 函数定义是这样的:输入一个节点 head,将「以 head 为起点」的链表反转,并返回反转之后的头结点。
quote: Labuladong 的翻转链表集合
想通递归函数定义后就很好实现了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
return reverse(head);
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode cur) {
if (cur == null || cur.next == null) return cur;
ListNode last = reverse(cur.next);
cur.next.next = cur;
cur.next = null;
return last;
}
}
|
24. 两两交换链表中的节点
使用虚拟头节点来大幅简化问题的一道模拟题:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
dummyHead.next = head;
ListNode prev = dummyHead;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null && cur.next != null) {
ListNode secondNode = cur.next;
cur.next = secondNode.next;
secondNode.next = cur;
prev.next = secondNode;
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
private void helperPrint(ListNode head) {
ListNode dm = head;
while (dm != null) {
System.out.print(dm.val + "->");
dm = dm.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
|
19.删除链表的倒数第N个节点
写做链表,但其实本质还是双指针 - 快慢指针的一道应用题:
如果要删除倒数第n个节点,让fast移动n步,然后让fast和slow同时移动,直到fast指向链表末尾。删掉slow所指向的节点就可以了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dmh = new ListNode(-1);
dmh.next = head;
ListNode fast = dmh;
ListNode slow = dmh;
int k = n;
while (k > 0) {
fast = fast.next;
k--;
}
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return dmh.next;
}
private void printHelper(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val + "->");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
|
面试题 02.07.链表相交
其实还是双指针但是要先找长的链表要先移动几步从而可以让两条链表同一起点:
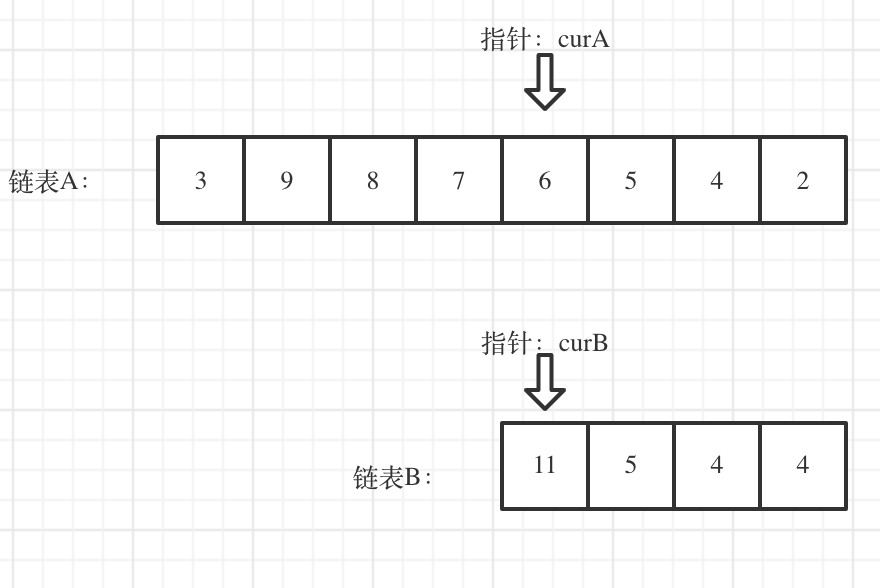
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
| public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode curLong = headA, curShort = headB;
int lenLong = 0, lenShort = 0;
while (curLong != null) {
lenLong++;
curLong = curLong.next;
}
while (curShort != null) {
lenShort++;
curShort = curShort.next;
}
curLong = headA;
curShort = headB;
if (lenShort > lenLong) {
int temp = lenShort;
lenShort = lenLong;
lenLong = temp;
ListNode tempNode = curLong;
curLong = curShort;
curShort = tempNode;
}
int gap = lenLong - lenShort;
while (gap > 0) {
curLong = curLong.next;
gap--;
}
while (curLong != null && curShort != null) {
if (curLong == curShort) return curLong;
curLong = curLong.next;
curShort = curShort.next;
}
return null;
}
private void printHelper(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val + "->");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
|
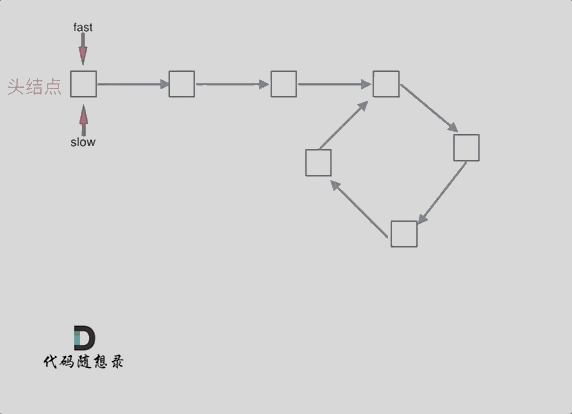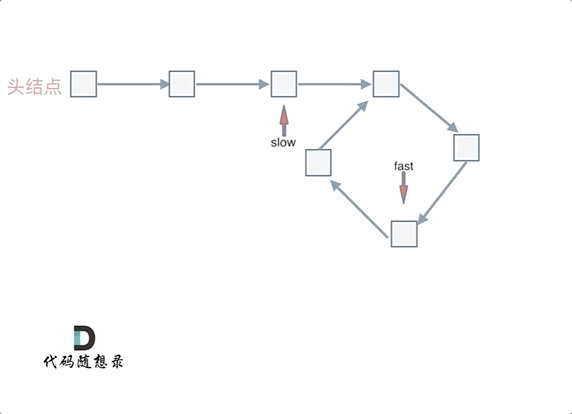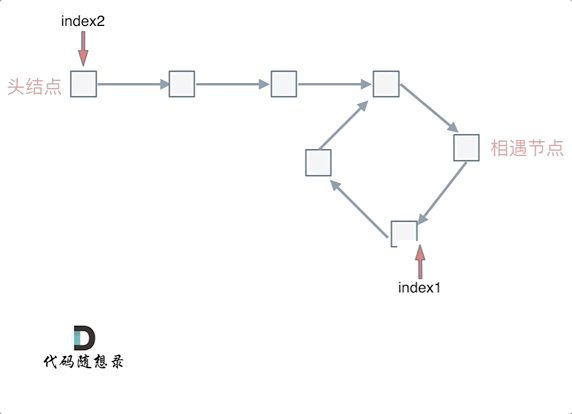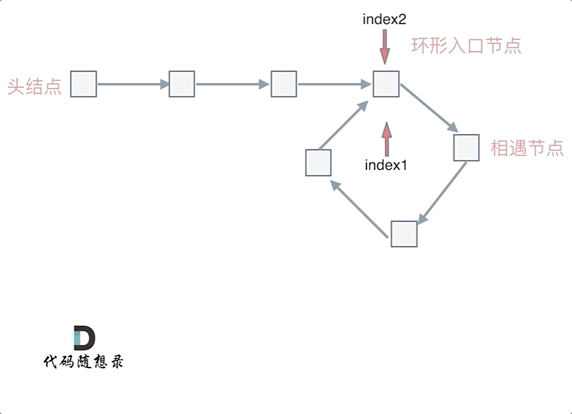
142.环形链表II
考察的其实还是双指针 - 快慢指针,但是加了一点数学。
需要做到两点:
判断链表是否含有环
- 使用快慢指针法,分别定义 fast 和 slow 指针,从头结点出发,fast指针每次移动两个节点,slow指针每次移动一个节点,如果 fast 和 slow指针在途中相遇 ,说明这个链表有环。
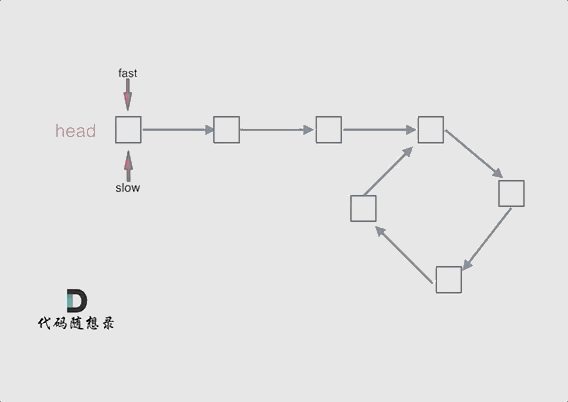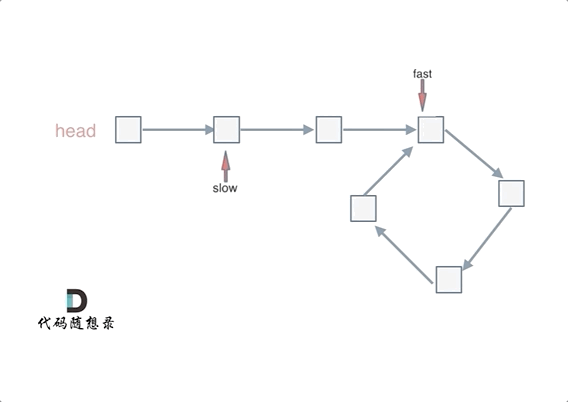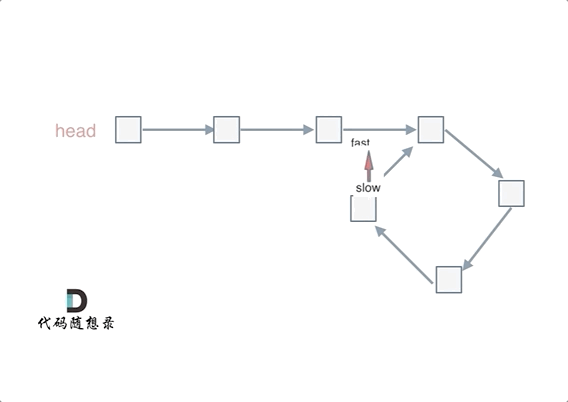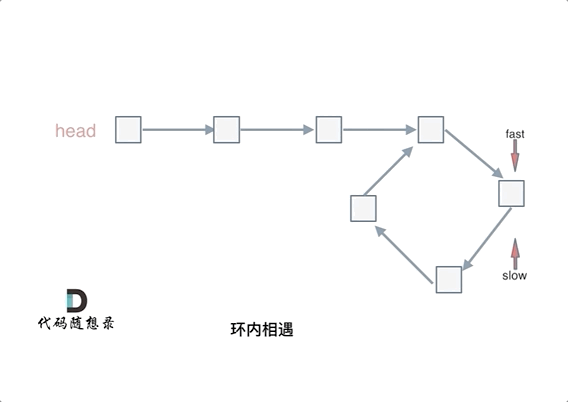
若有环,怎么找环开始的地方
- 从头结点出发一个指针,从相遇节点 也出发一个指针,这两个指针每次只走一个节点, 那么当这两个指针相遇的时候就是 环形入口的节点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast == slow) {
ListNode idxStart = head, meetStart = fast;
while (idxStart != meetStart) {
idxStart = idxStart.next;
meetStart = meetStart.next;
}
return idxStart;
}
}
return null;
}
}
|